Inositol pyrophosphates regulate cell growth and the environmental stress response by activating the HDAC Rpd3L
- PMID: 23643537
- PMCID: PMC3672359
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.03.043
Inositol pyrophosphates regulate cell growth and the environmental stress response by activating the HDAC Rpd3L
Abstract
Cells respond to stress and starvation by adjusting their growth rate and enacting stress defense programs. In eukaryotes this involves inactivation of TORC1, which in turn triggers downregulation of ribosome and protein synthesis genes and upregulation of stress response genes. Here we report that the highly conserved inositol pyrophosphate (PP-IP) second messengers (including 1-PP-IP5, 5-PP-IP4, and 5-PP-IP5) are also critical regulators of cell growth and the general stress response, acting in parallel with the TORC1 pathway to control the activity of the class I histone deacetylase Rpd3L. In fact, yeast cells that cannot synthesize any of the PP-IPs mount little to no transcriptional response to osmotic, heat, or oxidative stress. Furthermore, PP-IP-dependent regulation of Rpd3L occurs independently of the role individual PP-IPs (such as 5-PP-IP5) play in activating specialized stress/starvation response pathways. Thus, the PP-IP second messengers simultaneously activate and tune the global response to stress and starvation signals.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
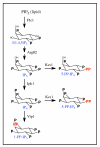
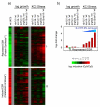
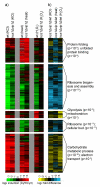
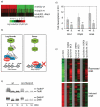
Similar articles
-
The intersection between stress responses and inositol pyrophosphates in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Curr Genet. 2020 Oct;66(5):901-910. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01078-8. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 32322930 Review.
-
Inositol pyrophosphates regulate RNA polymerase I-mediated rRNA transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochem J. 2015 Feb 15;466(1):105-14. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140798. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 25423617 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of the TORC1 and Osmotic Stress Signaling Network in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.G3 (Bethesda). 2015 Dec 17;6(2):463-74. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.025882. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 26681516 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol pyrophosphates modulate hydrogen peroxide signalling.Biochem J. 2009 Sep 14;423(1):109-18. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090241. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19614566
-
Inositol Pyrophosphates: Signaling Molecules with Pleiotropic Actions in Mammals.Molecules. 2020 May 8;25(9):2208. doi: 10.3390/molecules25092208. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32397291 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 1 (IP6K1) reduces cell migration and invasion, conferring protection from aerodigestive tract carcinoma in mice.Cell Signal. 2016 Aug;28(8):1124-36. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.04.011. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Cell Signal. 2016. PMID: 27140681 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol polyphosphates regulate and predict yeast pseudohyphal growth phenotypes.PLoS Genet. 2018 Jun 25;14(6):e1007493. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007493. eCollection 2018 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29939992 Free PMC article.
-
Towards pharmacological intervention in inositol pyrophosphate signalling.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Feb;44(1):191-6. doi: 10.1042/BST20150184. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 26862205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolutionary engineering of a wine yeast strain revealed a key role of inositol and mannoprotein metabolism during low-temperature fermentation.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jul 22;16(1):537. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1755-2. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26194190 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid stimulation of cellular Pi uptake by the inositol pyrophosphate InsP8 induced by its photothermal release from lipid nanocarriers using a near infra-red light-emitting diode.Chem Sci. 2020 Sep 8;11(37):10265-10278. doi: 10.1039/d0sc02144j. eCollection 2020 Oct 7. Chem Sci. 2020. PMID: 33659052 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

