Identification and characterisation of functional expressed sequence tags-derived simple sequence repeat (eSSR) markers for genetic linkage mapping of Schistosoma mansoni juvenile resistance and susceptibility loci in Biomphalaria glabrata
- PMID: 23643514
- PMCID: PMC4038333
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2013.03.007
Identification and characterisation of functional expressed sequence tags-derived simple sequence repeat (eSSR) markers for genetic linkage mapping of Schistosoma mansoni juvenile resistance and susceptibility loci in Biomphalaria glabrata
Abstract
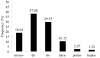
Biomphalaria glabrata susceptibility to Schistosoma mansoni has a strong genetic component, offering the possibility for investigating host-parasite interactions at the molecular level, perhaps leading to novel control approaches. The identification, mapping and molecular characterisation of genes that influence the outcome of parasitic infection in the intermediate snail host is, therefore, seen as fundamental to the control of schistosomiasis. To better understand the evolutionary processes driving disease resistance/susceptibility phenotypes, we previously identified polymorphic random amplification of polymorphic DNA and genomic simple sequence repeats from B. glabrata. In the present study we identified and characterised polymorphic expressed simple sequence repeats markers (Bg-eSSR) from existing B. glabrata expressed sequence tags. Using these markers, and with previously identified genomic simple sequence repeats, genetic linkage mapping for parasite refractory and susceptibility phenotypes, the first known for B. glabrata, was initiated. Data mining of 54,309 expressed sequence tag, produced 660 expressed simple sequence repeats of which dinucleotide motifs (TA)n were the most common (37.88%), followed by trinucleotide (29.55%), mononucleotide (18.64%) and tetranucleotide (10.15%). Penta- and hexanucleotide motifs represented <3% of the Bg-eSSRs identified. While the majority (71%) of Bg-eSSRs were monomorphic between resistant and susceptible snails, several were, however, useful for the construction of a genetic linkage map based on their inheritance in segregating F2 progeny snails derived from crossing juvenile BS-90 and NMRI snails. Polymorphic Bg-eSSRs assorted into six linkage groups at a logarithm of odds score of 3. Interestingly, the heritability of four markers (Prim1_910, Prim1_771, Prim6_1024 and Prim7_823) with juvenile snail resistance were, by t-test, significant (P<0.05) while an allelic marker, Prim24_524, showed linkage with the juvenile snail susceptibility phenotype. On the basis of our results it is possible that the gene(s) controlling juvenile resistance and susceptibility to S. mansoni infection in B. glabrata are not only on the same linkage group but lie within a short distance (42cM) of each other.
Copyright © 2013 Australian Society for Parasitology Inc. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
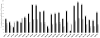
Similar articles
-
PIWI silencing mechanism involving the retrotransposon nimbus orchestrates resistance to infection with Schistosoma mansoni in the snail vector, Biomphalaria glabrata.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Sep 8;15(9):e0009094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009094. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34495959 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular approaches in the study of Biomphalaria glabrata--Schistosoma mansoni interactions: linkage analysis and gene expression profiling.Parasitology. 2001;123 Suppl:S181-96. doi: 10.1017/s0031182001008174. Parasitology. 2001. PMID: 11769282 Review.
-
Reversing the resistance phenotype of the Biomphalaria glabrata snail host Schistosoma mansoni infection by temperature modulation.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(4):e1002677. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002677. Epub 2012 Apr 26. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22577362 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of immediate response genes dominantly expressed in juvenile resistant and susceptible Biomphalaria glabrata snails upon exposure to Schistosoma mansoni.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2010 Jan;169(1):27-39. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2009.09.009. Epub 2009 Oct 6. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2010. PMID: 19815034 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modulation, stress and plasticity in susceptibility of the snail host, Biomphalaria glabrata, to Schistosoma mansoni infection.Int J Parasitol. 2016 Jun;46(7):389-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2016.03.003. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Int J Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27056272 Review.
Cited by
-
Host genetic backgrounds: the key to determining parasite-host adaptation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Aug 10;13:1228206. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1228206. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37637465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Scan and Test of Candidate Genes in the Snail Biomphalaria glabrata Reveal New Locus Influencing Resistance to Schistosoma mansoni.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015 Sep 15;9(9):e0004077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004077. eCollection 2015. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015. PMID: 26372103 Free PMC article.
-
A Targeted Capture Linkage Map Anchors the Genome of the Schistosomiasis Vector Snail, Biomphalaria glabrata.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Jul 5;7(7):2353-2361. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.041319. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28526730 Free PMC article.
-
PIWI silencing mechanism involving the retrotransposon nimbus orchestrates resistance to infection with Schistosoma mansoni in the snail vector, Biomphalaria glabrata.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Sep 8;15(9):e0009094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009094. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34495959 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance of Biomphalaria glabrata 13-16-R1 snails to Schistosoma mansoni PR1 is a function of haemocyte abundance and constitutive levels of specific transcripts in haemocytes.Int J Parasitol. 2014 May;44(6):343-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2013.11.004. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Int J Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 24681237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adema CM, Luo MZ, Hanelt B, Hertel LA, Marshall JJ, Zhang SM, DeJong RJ, Kim HR, Kudrna D, Wing RA, Soderlund C, Knight M, Lewis FA, Caldeira RL, Jannotti-Passos LK, Carvalho Odos S, Loker ES. A bacterial artificial chromosome library for Biomphalaria glabrata, intermediate snail host of Schistosoma mansoni. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2006;101 (Suppl 1):167–177. - PubMed
-
- Aisemberg J, Nahabedian DE, Wider EA, Verrengia Guerrero NR. Comparative study on two freshwater invertebrates for monitoring environmental lead exposure. Toxicology. 2005;210:45–53. - PubMed
-
- Ansaldo M, Nahabedian DE, Di Fonzo C, Wider EA. Effect of cadmium, lead and arsenic on the oviposition, hatching and embryonic survival of Biomphalaria glabrata. Sci Total Environ. 2009;407:1923–1928. - PubMed
-
- Bajpai A, Sridhar S, Reddy HM, Jesudasan RA. BRM-Parser: a tool for comprehensive analysis of BLAST and RepeatMasker results. In Silico Biol. 2007;7:399–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

