Components of the canonical and non-canonical Wnt pathways are not mis-expressed in pituitary tumors
- PMID: 23638078
- PMCID: PMC3637156
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062424
Components of the canonical and non-canonical Wnt pathways are not mis-expressed in pituitary tumors
Abstract
Introduction: Canonical and non-canonical Wnt pathways are involved in the genesis of multiple tumors; however, their role in pituitary tumorigenesis is mostly unknown.
Objective: This study evaluated gene and protein expression of Wnt pathways in pituitary tumors and whether these expression correlate to clinical outcome.
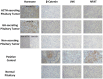
Materials and methods: Genes of the WNT canonical pathway: activating ligands (WNT11, WNT4, WNT5A), binding inhibitors (DKK3, sFRP1), β-catenin (CTNNB1), β-catenin degradation complex (APC, AXIN1, GSK3β), inhibitor of β-catenin degradation complex (AKT1), sequester of β-catenin (CDH1), pathway effectors (TCF7, MAPK8, NFAT5), pathway mediators (DVL-1, DVL-2, DVL-3, PRICKLE, VANGL1), target genes (MYB, MYC, WISP2, SPRY1, TP53, CCND1); calcium dependent pathway (PLCB1, CAMK2A, PRKCA, CHP); and planar cell polarity pathway (PTK7, DAAM1, RHOA) were evaluated by QPCR, in 19 GH-, 18 ACTH-secreting, 21 non-secreting (NS) pituitary tumors, and 5 normal pituitaries. Also, the main effectors of canonical (β-catenin), planar cell polarity (JNK), and calcium dependent (NFAT5) Wnt pathways were evaluated by immunohistochemistry.
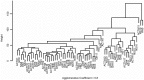
Results: There are no differences in gene expression of canonical and non-canonical Wnt pathways between all studied subtypes of pituitary tumors and normal pituitaries, except for WISP2, which was over-expressed in ACTH-secreting tumors compared to normal pituitaries (4.8x; p = 0.02), NS pituitary tumors (7.7x; p = 0.004) and GH-secreting tumors (5.0x; p = 0.05). β-catenin, NFAT5 and JNK proteins showed no expression in normal pituitaries and in any of the pituitary tumor subtypes. Furthermore, no association of the studied gene or protein expression was observed with tumor size, recurrence, and progressive disease. The hierarchical clustering showed a regular pattern of genes of the canonical and non-canonical Wnt pathways randomly distributed throughout the dendrogram.
Conclusions: Our data reinforce previous reports suggesting no activation of canonical Wnt pathway in pituitary tumorigenesis. Moreover, we describe, for the first time, evidence that non-canonical Wnt pathways are also not mis-expressed in the pituitary tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of the Canonical Wnt Pathway Activation on the Pathogenesis and Prognosis of Adamantinomatous Craniopharyngiomas.Horm Metab Res. 2018 Jul;50(7):575-581. doi: 10.1055/a-0593-5956. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Horm Metab Res. 2018. PMID: 29625497
-
Wnt/beta-catenin pathway deregulation in childhood adrenocortical tumors.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Oct;96(10):3106-14. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-0363. Epub 2011 Aug 17. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21849527
-
Altered expression of noncanonical Wnt pathway genes in paediatric and adult adrenocortical tumours.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014 Oct;81(4):503-10. doi: 10.1111/cen.12462. Epub 2014 May 19. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014. PMID: 24717047
-
Identification of Wnt family inhibitors: a pituitary tumor directed whole genome approach.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010 Sep 15;326(1-2):48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.02.039. Epub 2010 Mar 6. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20211224 Review.
-
Interaction of the Wnt/β-catenin and RAS-ERK pathways involving co-stabilization of both β-catenin and RAS plays important roles in the colorectal tumorigenesis.Adv Biol Regul. 2018 May;68:46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2018.01.001. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Adv Biol Regul. 2018. PMID: 29449169 Review.
Cited by
-
Ptk7 and Mcc, Unfancied Components in Non-Canonical Wnt Signaling and Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2016 Jul 16;8(7):68. doi: 10.3390/cancers8070068. Cancers (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27438854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary cilia modulate balance of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling responses in the injured kidney.Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2015 Apr 16;8:6. doi: 10.1186/s13069-015-0024-y. eCollection 2015. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2015. PMID: 25901180 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the CCN protein family in cancer.BMB Rep. 2018 Oct;51(10):486-492. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2018.51.10.192. BMB Rep. 2018. PMID: 30158025 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of CCN family proteins in tumorigenesis and cancer metastasis (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2015 Dec;36(6):1451-63. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2390. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26498181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The identification of human pituitary adenoma-initiating cells.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2016 Nov 28;4(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s40478-016-0394-4. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2016. PMID: 27894339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Melmed S (2011) Pathogenesis of pituitary tumors. Nature reviews Endocrinology 7: 257–266. - PubMed
-
- Kaltsas GA, Kola B, Borboli N, Morris DG, Gueorguiev M, et al. (2002) Sequence analysis of the PRKAR1A gene in sporadic somatotroph and other pituitary tumours. Clinical endocrinology 57: 443–448. - PubMed
-
- Zhuang Z, Ezzat SZ, Vortmeyer AO, Weil R, Oldfield EH, et al. (1997) Mutations of the MEN1 tumor suppressor gene in pituitary tumors. Cancer research 57: 5446–5451. - PubMed
-
- Vierimaa O, Georgitsi M, Lehtonen R, Vahteristo P, Kokko A, et al. (2006) Pituitary adenoma predisposition caused by germline mutations in the AIP gene. Science (New York, NY) 312: 1228–1230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

