Modelling the regulation of telomere length: the effects of telomerase and G-quadruplex stabilising drugs
- PMID: 23620229
- PMCID: PMC3975128
- DOI: 10.1007/s00285-013-0678-2
Modelling the regulation of telomere length: the effects of telomerase and G-quadruplex stabilising drugs
Abstract
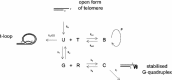
Telomeres are guanine-rich sequences at the end of chromosomes which shorten during each replication event and trigger cell cycle arrest and/or controlled death (apoptosis) when reaching a threshold length. The enzyme telomerase replenishes the ends of telomeres and thus prolongs the life span of cells, but also causes cellular immortalisation in human cancer. G-quadruplex (G4) stabilising drugs are a potential anticancer treatment which work by changing the molecular structure of telomeres to inhibit the activity of telomerase. We investigate the dynamics of telomere length in different conformational states, namely t-loops, G-quadruplex structures and those being elongated by telomerase. By formulating deterministic differential equation models we study the effects of various levels of both telomerase and concentrations of a G4-stabilising drug on the distribution of telomere lengths, and analyse how these effects evolve over large numbers of cell generations. As well as calculating numerical solutions, we use quasicontinuum methods to approximate the behaviour of the system over time, and predict the shape of the telomere length distribution. We find those telomerase and G4-concentrations where telomere length maintenance is successfully regulated. Excessively high levels of telomerase lead to continuous telomere lengthening, whereas large concentrations of the drug lead to progressive telomere erosion. Furthermore, our models predict a positively skewed distribution of telomere lengths, that is, telomeres accumulate over lengths shorter than the mean telomere length at equilibrium. Our model results for telomere length distributions of telomerase-positive cells in drug-free assays are in good agreement with the limited amount of experimental data available.
Figures

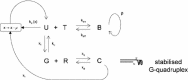


Similar articles
-
Stabilization of Telomere G-Quadruplexes Interferes with Human Herpesvirus 6A Chromosomal Integration.J Virol. 2017 Jun 26;91(14):e00402-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00402-17. Print 2017 Jul 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28468887 Free PMC article.
-
Telomere targeting with a novel G-quadruplex-interactive ligand BRACO-19 induces T-loop disassembly and telomerase displacement in human glioblastoma cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 22;7(12):14925-39. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7483. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26908447 Free PMC article.
-
The G-quadruplex-interactive molecule BRACO-19 inhibits tumor growth, consistent with telomere targeting and interference with telomerase function.Cancer Res. 2005 Feb 15;65(4):1489-96. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2910. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15735037
-
Oligonucleotides and G-quadruplex stabilizers: targeting telomeres and telomerase in cancer therapy.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(41):6422-37. doi: 10.2174/1381612820666140630100702. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24975605 Review.
-
Telomere length homeostasis.Chromosoma. 2006 Dec;115(6):413-25. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0067-3. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Chromosoma. 2006. PMID: 16741708 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and Molecular Dynamic Simulation of Novel Cationic and Non-cationic Pyrimidine Derivatives as Potential G-quadruplex-ligands.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024;24(15):1126-1141. doi: 10.2174/0118715206291797240523112439. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38840398
-
Evaluating biomarkers to model cancer risk post cosmic ray exposure.Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2016 Jun;9:19-47. doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2016.05.004. Epub 2016 May 21. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2016. PMID: 27345199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stochastic simulations of normal aging and Werner's syndrome.Bull Math Biol. 2014 Jun;76(6):1241-69. doi: 10.1007/s11538-014-9952-8. Epub 2014 Apr 26. Bull Math Biol. 2014. PMID: 24771273 Free PMC article.
-
Mathematical modelling of telomere length dynamics.J Math Biol. 2020 Mar;80(4):1039-1076. doi: 10.1007/s00285-019-01448-y. Epub 2019 Nov 14. J Math Biol. 2020. PMID: 31728621 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

