Habitat-specific shaping of proliferation and neuronal differentiation in adult hippocampal neurogenesis of wild rodents
- PMID: 23616743
- PMCID: PMC3629335
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00059
Habitat-specific shaping of proliferation and neuronal differentiation in adult hippocampal neurogenesis of wild rodents
Abstract
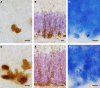
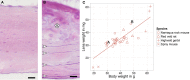
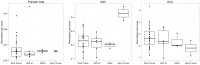
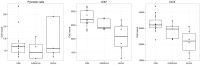
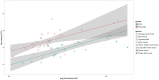
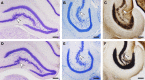
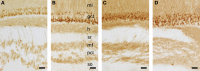
Daily life of wild mammals is characterized by a multitude of attractive and aversive stimuli. The hippocampus processes complex polymodal information associated with such stimuli and mediates adequate behavioral responses. How newly generated hippocampal neurons in wild animals contribute to hippocampal function is still a subject of debate. Here, we test the relationship between adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN) and habitat types. To this end, we compare wild Muridae species of southern Africa [Namaqua rock mouse (Micaelamys namaquensis), red veld rat (Aethomys chrysophilus), highveld gerbil (Tatera brantsii), and spiny mouse (Acomys spinosissimus)] with data from wild European Muridae [long-tailed wood mice (Apodemus sylvaticus), pygmy field mice (Apodemus microps), yellow-necked wood mice (Apodemus flavicollis), and house mice (Mus musculus domesticus)] from previous studies. The pattern of neurogenesis, expressed in normalized numbers of Ki67- and Doublecortin(DCX)-positive cells to total granule cells (GCs), is similar for the species from a southern African habitat. However, we found low proliferation, but high neuronal differentiation in rodents from the southern African habitat compared to rodents from the European environment. Within the African rodents, we observe additional regulatory and morphological traits in the hippocampus. Namaqua rock mice with previous pregnancies showed lower AHN compared to males and nulliparous females. The phylogenetically closely related species (Namaqua rock mouse and red veld rat) show a CA4, which is not usually observed in murine rodents. The specific features of the southern environment that may be associated with the high number of young neurons in African rodents still remain to be elucidated. This study provides the first evidence that a habitat can shape adult neurogenesis in rodents across phylogenetic groups.
Keywords: CA4; Ki67; Muridae; doublecortin; gender; habitat; hippocampus; neurogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Strain and Species on the Septo-Temporal Distribution of Adult Neurogenesis in Rodents.Front Neurosci. 2017 Dec 19;11:719. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00719. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29311796 Free PMC article.
-
No effect of running and laboratory housing on adult hippocampal neurogenesis in wild caught long-tailed wood mouse.BMC Neurosci. 2009 May 6;10:43. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-10-43. BMC Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19419549 Free PMC article.
-
Marked species and age-dependent differences in cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the hippocampus of wild-living rodents.Hippocampus. 2004;14(8):1000-10. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20018. Hippocampus. 2004. PMID: 15390172
-
Comparing adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mammalian species and orders: influence of chronological age and life history stage.Eur J Neurosci. 2011 Sep;34(6):978-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07804.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21929629 Review.
-
Running in laboratory and wild rodents: differences in context sensitivity and plasticity of hippocampal neurogenesis.Behav Brain Res. 2012 Feb 14;227(2):363-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.04.027. Epub 2011 Apr 27. Behav Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 21549157 Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of early-life and intergenerational stress on the brain.Proc Biol Sci. 2023 Nov 29;290(2011):20231356. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2023.1356. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Proc Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38018110 Free PMC article.
-
Septo-temporal distribution and lineage progression of hippocampal neurogenesis in a primate (Callithrix jacchus) in comparison to mice.Front Neuroanat. 2015 Jun 29;9:85. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2015.00085. eCollection 2015. Front Neuroanat. 2015. PMID: 26175670 Free PMC article.
-
Adult neurogenesis and its anatomical context in the hippocampus of three mole-rat species.Front Neuroanat. 2014 May 20;8:39. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2014.00039. eCollection 2014. Front Neuroanat. 2014. PMID: 24904308 Free PMC article.
-
Adult hippocampal neurogenesis in natural populations of mammals.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 May 1;7(5):a021295. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021295. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 25934014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NECAB1-3, parvalbumin, calbindin, and calretinin in the hippocampus of the European mole.Front Neuroanat. 2024 Sep 4;18:1452722. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2024.1452722. eCollection 2024. Front Neuroanat. 2024. PMID: 39296922 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

