Rnf165/Ark2C enhances BMP-Smad signaling to mediate motor axon extension
- PMID: 23610558
- PMCID: PMC3627648
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001538
Rnf165/Ark2C enhances BMP-Smad signaling to mediate motor axon extension
Abstract
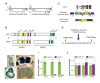
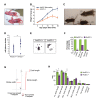
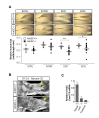
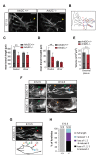
Little is known about extrinsic signals required for the advancement of motor neuron (MN) axons, which extend over long distances in the periphery to form precise connections with target muscles. Here we present that Rnf165 (Arkadia-like; Arkadia2; Ark2C) is expressed specifically in the nervous system and that its loss in mice causes motor innervation defects that originate during development and lead to wasting and death before weaning. The defects range from severe reduction of motor axon extension as observed in the dorsal forelimb to shortening of presynaptic branches of the phrenic nerve, as observed in the diaphragm. Molecular functional analysis showed that in the context of the spinal cord Ark2C enhances transcriptional responses of the Smad1/5/8 effectors, which are activated (phosphorylated) downstream of Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signals. Consistent with Ark2C-modulated BMP signaling influencing motor axons, motor pools in the spinal cord were found to harbor phosphorylated Smad1/5/8 (pSmad) and treatment of primary MN with BMP inhibitor diminished axon length. In addition, genetic reduction of BMP-Smad signaling in Ark2C (+/-) mice caused the emergence of Ark2C (-/-) -like dorsal forelimb innervation deficits confirming that enhancement of BMP-Smad responses by Ark2C mediates efficient innervation. Together the above data reveal an involvement of BMP-Smad signaling in motor axon advancement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of Olig2 precursors by FGF involves BMP signalling blockade at the Smad level.PLoS One. 2008 Aug 6;3(8):e2863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002863. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18682850 Free PMC article.
-
BMP/SMAD Pathway Promotes Neurogenesis of Midbrain Dopaminergic Neurons In Vivo and in Human Induced Pluripotent and Neural Stem Cells.J Neurosci. 2018 Feb 14;38(7):1662-1676. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1540-17.2018. Epub 2018 Jan 10. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29321139 Free PMC article.
-
The bone morphogenetic protein axis is a positive regulator of skeletal muscle mass.J Cell Biol. 2013 Oct 28;203(2):345-57. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201211134. Epub 2013 Oct 21. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24145169 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
-
Crossing the border: molecular control of motor axon exit.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(12):8539-61. doi: 10.3390/ijms12128539. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22272090 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
BMP signaling in axon regeneration.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014 Aug;27:127-34. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2014.03.009. Epub 2014 Apr 10. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24713578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Split Hand/Foot Malformation Associated with 7q21.3 Microdeletion: A Case Report.Mol Syndromol. 2016 Feb;6(6):287-96. doi: 10.1159/000443708. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Mol Syndromol. 2016. PMID: 27022330 Free PMC article.
-
A low affinity cis-regulatory BMP response element restricts target gene activation to subsets of Drosophila neurons.Elife. 2020 Oct 30;9:e59650. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59650. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33124981 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein signaling in vertebrate motor neurons and neuromuscular communication.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jan 27;8:453. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00453. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25674047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-stranded γPNAs for in vivo site-specific genome editing via Watson-Crick recognition.Curr Gene Ther. 2014;14(5):331-42. doi: 10.2174/1566523214666140825154158. Curr Gene Ther. 2014. PMID: 25174576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hippenmeyer S, Kramer I, Arber S (2004) Control of neuronal phenotype: what targets tell the cell bodies. Trends Neurosci 27: 482–488. - PubMed
-
- Salie R, Niederkofler V, Arber S (2005) Patterning molecules; multitasking in the nervous system. Neuron 45: 189–192. - PubMed
-
- Shirasaki R, Pfaff SL (2002) Transcriptional codes and the control of neuronal identity. Annu Rev Neurosci 25: 251–281. - PubMed
-
- Rossi F, Gianola S, Corvetti L (2007) Regulation of intrinsic neuronal properties for axon growth and regeneration. Progress in neurobiology 81: 1–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

