MicroRNA transcriptomes relate intermuscular adipose tissue to metabolic risk
- PMID: 23609494
- PMCID: PMC3645765
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms14048611
MicroRNA transcriptomes relate intermuscular adipose tissue to metabolic risk
Abstract
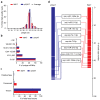
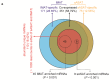
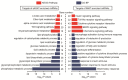
Intermuscular adipose tissue is located between the muscle fiber bundles in skeletal muscles, and has similar metabolic features to visceral adipose tissue, which has been found to be related to a number of obesity-related diseases. Although various miRNAs are known to play crucial roles in adipose deposition and adipogenesis, the microRNA transcriptome of intermuscular adipose tissue has not, until now, been studied. Here, we sequenced the miRNA transcriptomes of porcine intermuscular adipose tissue by small RNA-sequencing and compared it to a representative subcutaneous adipose tissue. We found that the inflammation- and diabetes-related miRNAs were significantly enriched in the intermuscular rather than in the subcutaneous adipose tissue. A functional enrichment analysis of the genes predicted to be targeted by the enriched miRNAs also indicated that intermuscular adipose tissue was associated mainly with immune and inflammation responses. Our results suggest that the intermuscular adipose tissue should be recognized as a potential metabolic risk factor of obesity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intrinsic features in microRNA transcriptomes link porcine visceral rather than subcutaneous adipose tissues to metabolic risk.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 6;8(11):e80041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080041. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24223210 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and characterization of microRNAs from porcine skeletal muscle and adipose tissue.Mol Biol Rep. 2010 Oct;37(7):3567-74. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0005-6. Epub 2010 Feb 24. Mol Biol Rep. 2010. PMID: 20180025
-
Identification and comparison of microRNAs from skeletal muscle and adipose tissues from two porcine breeds.Anim Genet. 2012 Dec;43(6):704-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.2012.02332.x. Epub 2012 Feb 27. Anim Genet. 2012. PMID: 22497549
-
Intermuscular adipose tissue in obesity and related disorders: cellular origins, biological characteristics and regulatory mechanisms.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 18;14:1280853. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1280853. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37920255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA regulatory networks in human adipose tissue and obesity.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015 May;11(5):276-88. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2015.25. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25732520 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in testes of Duroc and Meishan boars.BMC Genomics. 2020 Oct 2;21(1):686. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07096-7. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33008286 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric bypass surgery with exercise alters plasma microRNAs that predict improvements in cardiometabolic risk.Int J Obes (Lond). 2017 Jul;41(7):1121-1130. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2017.84. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Int J Obes (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28344345 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Intermuscular adipose tissue accumulation is associated with higher tissue sodium in healthy individuals.Physiol Rep. 2024 Jul;12(13):e16127. doi: 10.14814/phy2.16127. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38960895 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of histological and microRNA profiles changes in rabbit skin development.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 16;10(1):454. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-57327-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31949201 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating miRNA and mRNA Expression Profiling Uncovers miRNAs Underlying Fat Deposition in Sheep.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:1857580. doi: 10.1155/2017/1857580. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28293627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang Y., Proenca R., Maffei M., Barone M., Leopold L., Friedman J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994;372:425–432. - PubMed
-
- Lago F., Dieguez C., Gómez-Reino J., Gualillo O. The emerging role of adipokines as mediators of inflammation and immune responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007;18:313–325. - PubMed
-
- Arner P. Insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes-role of the adipokines. Curr. Mol. Med. 2005;5:333–339. - PubMed
-
- Dogru T., Sonmez A., Tasci I., Bozoglu E., Yilmaz M.I., Genc H., Erdem G., Gok M., Bingol N., Kilic S. Plasma visfatin levels in patients with newly diagnosed and untreated type 2 diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. Suppl. 2007;76:24–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

