Solution NMR refinement of a metal ion bound protein using metal ion inclusive restrained molecular dynamics methods
- PMID: 23609042
- PMCID: PMC3773525
- DOI: 10.1007/s10858-013-9729-7
Solution NMR refinement of a metal ion bound protein using metal ion inclusive restrained molecular dynamics methods
Abstract
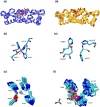
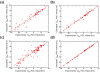
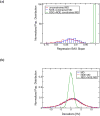
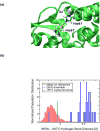
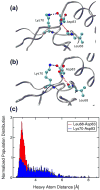
Correctly calculating the structure of metal coordination sites in a protein during the process of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) structure determination and refinement continues to be a challenging task. In this study, we present an accurate and convenient means by which to include metal ions in the NMR structure determination process using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations constrained by NMR-derived data to obtain a realistic and physically viable description of the metal binding site(s). This method provides the framework to accurately portray the metal ions and its binding residues in a pseudo-bond or dummy-cation like approach, and is validated by quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical (QM/MM) MD calculations constrained by NMR-derived data. To illustrate this approach, we refine the zinc coordination complex structure of the zinc sensing transcriptional repressor protein Staphylococcus aureus CzrA, generating over 130 ns of MD and QM/MM MD NMR-data compliant sampling. In addition to refining the first coordination shell structure of the Zn(II) ion, this protocol benefits from being performed in a periodically replicated solvation environment including long-range electrostatics. We determine that unrestrained (not based on NMR data) MD simulations correlated to the NMR data in a time-averaged ensemble. The accurate solution structure ensemble of the metal-bound protein accurately describes the role of conformational sampling in allosteric regulation of DNA binding by zinc and serves to validate our previous unrestrained MD simulations of CzrA. This methodology has potentially broad applicability in the structure determination of metal ion bound proteins, protein folding and metal template protein-design studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Studying allosteric regulation in metal sensor proteins using computational methods.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2014;96:181-218. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2014. PMID: 25443958 Review.
-
Simulations of allosteric motions in the zinc sensor CzrA.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Feb 22;134(7):3367-76. doi: 10.1021/ja208047b. Epub 2011 Nov 14. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22007899 Free PMC article.
-
Solution NMR structure of a designed metalloprotein and complementary molecular dynamics refinement.Structure. 2008 Feb;16(2):210-5. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2007.11.011. Structure. 2008. PMID: 18275812 Free PMC article.
-
Individual metal ligands play distinct functional roles in the zinc sensor Staphylococcus aureus CzrA.J Mol Biol. 2006 Mar 10;356(5):1124-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.12.019. Epub 2005 Dec 22. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16406068
-
Use of (113)Cd NMR to probe the native metal binding sites in metalloproteins: an overview.Met Ions Life Sci. 2013;11:117-44. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5179-8_6. Met Ions Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23430773 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of substrate dynamics in protein prenylation reactions.Acc Chem Res. 2015 Feb 17;48(2):439-48. doi: 10.1021/ar500321u. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Acc Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 25539152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YfeX - A New Platform for Carbene Transferase Development with High Intrinsic Reactivity.Chemistry. 2022 Nov 21;28(65):e202201474. doi: 10.1002/chem.202201474. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Chemistry. 2022. PMID: 35948517 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and mechanistic basis for redox sensing by the cyanobacterial transcription regulator RexT.Commun Biol. 2022 Mar 28;5(1):275. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03226-x. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35347217 Free PMC article.
-
Training data composition affects performance of protein structure analysis algorithms.Pac Symp Biocomput. 2022;27:10-21. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2022. PMID: 34890132 Free PMC article.
-
CHARMM-GUI 10 years for biomolecular modeling and simulation.J Comput Chem. 2017 Jun 5;38(15):1114-1124. doi: 10.1002/jcc.24660. Epub 2016 Nov 14. J Comput Chem. 2017. PMID: 27862047 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allen MP, Tildesley DJ. Computer Simulations of Liquids. Clarendon Press; Oxford: 1987.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

