Structure of active β-arrestin-1 bound to a G-protein-coupled receptor phosphopeptide
- PMID: 23604254
- PMCID: PMC3654799
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12120
Structure of active β-arrestin-1 bound to a G-protein-coupled receptor phosphopeptide
Abstract
The functions of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are primarily mediated and modulated by three families of proteins: the heterotrimeric G proteins, the G-protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) and the arrestins. G proteins mediate activation of second-messenger-generating enzymes and other effectors, GRKs phosphorylate activated receptors, and arrestins subsequently bind phosphorylated receptors and cause receptor desensitization. Arrestins activated by interaction with phosphorylated receptors can also mediate G-protein-independent signalling by serving as adaptors to link receptors to numerous signalling pathways. Despite their central role in regulation and signalling of GPCRs, a structural understanding of β-arrestin activation and interaction with GPCRs is still lacking. Here we report the crystal structure of β-arrestin-1 (also called arrestin-2) in complex with a fully phosphorylated 29-amino-acid carboxy-terminal peptide derived from the human V2 vasopressin receptor (V2Rpp). This peptide has previously been shown to functionally and conformationally activate β-arrestin-1 (ref. 5). To capture this active conformation, we used a conformationally selective synthetic antibody fragment (Fab30) that recognizes the phosphopeptide-activated state of β-arrestin-1. The structure of the β-arrestin-1-V2Rpp-Fab30 complex shows marked conformational differences in β-arrestin-1 compared to its inactive conformation. These include rotation of the amino- and carboxy-terminal domains relative to each other, and a major reorientation of the 'lariat loop' implicated in maintaining the inactive state of β-arrestin-1. These results reveal, at high resolution, a receptor-interacting interface on β-arrestin, and they indicate a potentially general molecular mechanism for activation of these multifunctional signalling and regulatory proteins.
Figures

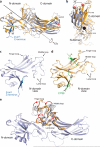
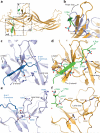
Comment in
-
Structural biology: Active arrestin proteins crystallized.Nature. 2013 May 2;497(7447):45-6. doi: 10.1038/nature12096. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Nature. 2013. PMID: 23604255 No abstract available.
-
Cell signalling: Crystallizing active arrestins.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;14(6):326. doi: 10.1038/nrm3592. Epub 2013 May 15. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23673968 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
β-Arrestin biosensors reveal a rapid, receptor-dependent activation/deactivation cycle.Nature. 2016 Mar 31;531(7596):661-4. doi: 10.1038/nature17198. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27007855 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of pre-activated arrestin p44.Nature. 2013 May 2;497(7447):142-6. doi: 10.1038/nature12133. Epub 2013 Apr 21. Nature. 2013. PMID: 23604253
-
Activation-dependent conformational changes in {beta}-arrestin 2.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 31;279(53):55744-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409785200. Epub 2004 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15501822
-
β-arrestins and G protein-coupled receptor trafficking.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;219:173-86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-41199-1_9. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24292830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Many faces of the GPCR-arrestin interaction.Arch Pharm Res. 2020 Sep;43(9):890-899. doi: 10.1007/s12272-020-01263-w. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Arch Pharm Res. 2020. PMID: 32803684 Review.
Cited by
-
Finding the Perfect Fit: Conformational Biosensors to Determine the Efficacy of GPCR Ligands.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022 Aug 14;5(9):694-709. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00256. eCollection 2022 Sep 9. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 36110374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The C-terminus region of β-arrestin1 modulates VE-cadherin expression and endothelial cell permeability.Cell Commun Signal. 2013 May 28;11(1):37. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-11-37. Cell Commun Signal. 2013. PMID: 23714586 Free PMC article.
-
Scaffolding of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling by β-Arrestins.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 17;23(2):1000. doi: 10.3390/ijms23021000. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35055186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 Receptor-Mediated Arrestin Translocation: Species, Subtype, and Agonist-Dependence.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Apr 10;10:350. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00350. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31024316 Free PMC article.
-
Biased M1 muscarinic receptor mutant mice show accelerated progression of prion neurodegenerative disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Dec 14;118(50):e2107389118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2107389118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34893539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pierce KL, Premont RT, Lefkowitz RJ. Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:639–650. doi:10.1038/nrm908. - PubMed
-
- Hepler JR, Gilman AG. G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992;17:383–387. - PubMed
-
- Freedman NJ, Lefkowitz RJ. Desensitization of G protein-coupled receptors. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1996;51:319–351. discussion 352-313. - PubMed
-
- Lefkowitz RJ, Shenoy SK. Transduction of receptor signals by beta-arrestins. Science. 2005;308:512–517. doi:10.1126/science.1109237. - PubMed
-
- Nobles KN, Guan Z, Xiao K, Oas TG, Lefkowitz RJ. The active conformation of beta-arrestin1: direct evidence for the phosphate sensor in the N-domain and conformational differences in the active states of beta-arrestins1 and -2. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:21370–21381. doi:10.1074/jbc.M611483200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- U54 GM074946/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL 075443/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM094588/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR011823/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL016037/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM087519/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM087519/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL075443/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070631/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL70631/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS028471/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HL16037/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM072688/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS028471/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GM072688/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS028471/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI_/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

