Loss of TCR-beta F1 and/or EZRIN expression is associated with unfavorable prognosis in nodal peripheral T-cell lymphomas
- PMID: 23599023
- PMCID: PMC3641318
- DOI: 10.1038/bcj.2013.10
Loss of TCR-beta F1 and/or EZRIN expression is associated with unfavorable prognosis in nodal peripheral T-cell lymphomas
Abstract
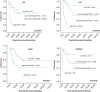
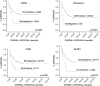
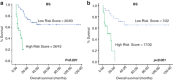
Nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma (nodal PTCL) has an unfavorable prognosis, and specific pathogenic alterations have not been fully identified. The biological and clinical relevance of the expression of CD30/T-cell receptor (TCR) genes is a topic under active investigation. One-hundred and ninety-three consecutive nodal PTCLs (89 angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphomas (AITL) and 104 PTCL-unspecified (PTCL-not otherwise specified (NOS)) cases) were analyzed for the immunohistochemical expression of 19 molecules, involving TCR/CD30 pathways and the associations with standard prognostic indices. Mutually exclusive expression was found between CD3 and TCR-beta F1 with CD30 expression. Taking all PTCL cases together, logistic regression identified a biological score (BS) including TCR molecules (TCR-beta F1 and EZRIN) that separates two subgroups of patients with a median survival of 34.57 and 5.20 months (P<0.001). Multivariate analysis identified BS and the prognostic index for PTCL (PIT) score as independent prognostic factors. This BS maintained its significance in multivariate analysis only for the PTCL-NOS subgroup of tumors. In AITL cases, only a high level of ki67 expression was related to prognosis. A BS including molecules involved in the TCR signaling pathway proved to be an independent prognostic factor of poor outcome in a multivariate analysis, specifically in PTCL-NOS patients. Nevertheless, validation in an independent series of homogeneously treated PTCL patients is required to confirm these data.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinicopathological implications of immunohistochemical expression of TBX21, CXCR3, GATA3, CCR4, and TCF1 in nodal follicular helper T-cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified.J Pathol Transl Med. 2024 Mar;58(2):59-71. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2024.01.04. Epub 2024 Jan 22. J Pathol Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38247153 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular profiling improves classification and prognostication of nodal peripheral T-cell lymphomas: results of a phase III diagnostic accuracy study.J Clin Oncol. 2013 Aug 20;31(24):3019-25. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.42.5611. Epub 2013 Jul 15. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23857971 Clinical Trial.
-
Serum IgA level, monocyte count, and international prognostic index are independently associated with overall survival in patients with HTLV-I-negative nodal peripheral T cell lymphoma.Ann Hematol. 2014 Jul;93(7):1185-91. doi: 10.1007/s00277-014-2025-0. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Ann Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24526138
-
Prognostic markers in peripheral T-cell lymphoma.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2010 Oct;5(4):222-8. doi: 10.1007/s11899-010-0062-x. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2010. PMID: 20690003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma--not otherwise specified.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011 Sep;79(3):321-9. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2010.07.007. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011. PMID: 20702104 Review.
Cited by
-
A three-signal model of T-cell lymphoma pathogenesis.Am J Hematol. 2016 Jan;91(1):113-22. doi: 10.1002/ajh.24203. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Am J Hematol. 2016. PMID: 26408334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T-cell receptor-δ expression and γδ+ T-cell infiltrates in primary cutaneous γδ T-cell lymphoma and other cutaneous T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders.Histopathology. 2018 Oct;73(4):653-662. doi: 10.1111/his.13671. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Histopathology. 2018. PMID: 29893430 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of Ezrin in Various Cancers: A Systematic Review and Updated Meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 3;5:17903. doi: 10.1038/srep17903. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26632332 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent presence of the PLCG1 S345F mutation in nodal peripheral T-cell lymphomas.Haematologica. 2015 Jan;100(1):e25-7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2014.113696. Epub 2014 Oct 10. Haematologica. 2015. PMID: 25304611 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Development of a Novel Clinical Prognostic Model for Patients With Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820964231. doi: 10.1177/1533033820964231. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 33073702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rizvi MA, Evens AM, Tallman MS, Nelson BP, Rosen ST. T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2006;107:1255–1264. - PubMed
-
- Vose J, Armitage J, Weisenburger D. International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: pathology findings and clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4124–4130. - PubMed
-
- Ballester B, Ramuz O, Gisselbrecht C, Doucet G, Loi L, Loriod B, et al. Gene expression profiling identifies molecular subgroups among nodal peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Oncogene. 2006;25:1560–1570. - PubMed
-
- de Leval L, Rickman DS, Thielen C, Reynies A, Huang YL, Delsol G, et al. The gene expression profile of nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma demonstrates a molecular link between angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) and follicular helper T (TFH) cells. Blood. 2007;109:4952–4963. - PubMed
-
- Aifantis I, Mandal M, Sawai K, Ferrando A, Vilimas T. Regulation of T-cell progenitor survival and cell-cycle entry by the pre-T-cell receptor. Immunol Rev. 2006;209:159–169. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

