Histone deacetylase inhibition reduces cardiac connexin43 expression and gap junction communication
- PMID: 23596417
- PMCID: PMC3625725
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2013.00044
Histone deacetylase inhibition reduces cardiac connexin43 expression and gap junction communication
Abstract
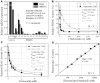
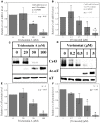
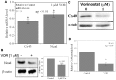
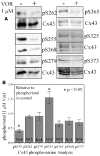
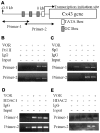
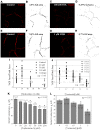
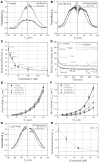
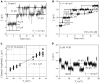
Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) are being investigated as novel therapies for cancer, inflammation, neurodegeneration, and heart failure. The effects of HDACIs on the functional expression of cardiac gap junctions (GJs) are essentially unknown. The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of trichostatin A (TSA) and vorinostat (VOR) on functional GJ expression in ventricular cardiomyocytes. The effects of HDAC inhibition on connexin43 (Cx43) expression and functional GJ assembly were examined in primary cultured neonatal mouse ventricular myocytes. TSA and VOR reduced Cx43 mRNA, protein expression, and immunolocalized Cx43 GJ plaque area within ventricular myocyte monolayer cultures in a dose-dependent manner. Chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments revealed altered protein interactions with the Cx43 promoter. VOR also altered the phosphorylation state of several key regulatory Cx43 phospho-serine sites. Patch clamp analysis revealed reduced electrical coupling between isolated ventricular myocyte pairs, altered transjunctional voltage-dependent inactivation kinetics, and steady state junctional conductance inactivation and recovery relationships. Single GJ channel conductance was reduced to 54 pS only by maximum inhibitory doses of TSA (≥ 100 nM). These two hydroxamate pan-HDACIs exert multiple levels of regulation on ventricular GJ communication by altering Cx43 expression, GJ area, post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation, acetylation), gating, and channel conductance. Although a 50% downregulation of Cx43 GJ communication alone may not be sufficient to slow ventricular conduction or induce arrhythmias, the development of class-selective HDACIs may help avoid the potential negative cardiovascular effects of pan-HDACI.
Keywords: connexin40; connexin43; gap junctions; phosphorylation; trichostatin A; vorinostat.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional formation of heterotypic gap junction channels by connexins-40 and -43.Channels (Austin). 2014;8(5):433-43. doi: 10.4161/19336950.2014.949188. Channels (Austin). 2014. PMID: 25483586 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in cardiac Nav1.5 expression, function, and acetylation by pan-histone deacetylase inhibitors.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;311(5):H1139-H1149. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00156.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27638876 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Functional Expression of Connexin43 and NaV1.5 by Pan- and Class-Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibition in Heart.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 4;19(8):2288. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082288. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30081552 Free PMC article.
-
Is the junctional uncoupling elicited in rat ventricular myocytes by some dephosphorylation treatments due to changes in the phosphorylation status of Cx43?Eur Biophys J. 2004 May;33(3):201-10. doi: 10.1007/s00249-003-0381-0. Epub 2004 Jan 27. Eur Biophys J. 2004. PMID: 14745523 Review.
-
[Remodeling of cardiac gap junctions and arrhythmias].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2011 Dec 25;63(6):586-92. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 22193455 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Detrimental effect of class-selective histone deacetylase inhibitors during tissue regeneration following hindlimb ischemia.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 9;288(32):22915-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.484337. Epub 2013 Jul 7. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23836913 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine acetyltransferases and lysine deacetylases as targets for cardiovascular disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020 Feb;17(2):96-115. doi: 10.1038/s41569-019-0235-9. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 31350538 Review.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms of Aging and Aging-Associated Diseases.Cells. 2023 Apr 14;12(8):1163. doi: 10.3390/cells12081163. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37190071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mind the gap! Connexins and pannexins in physiology, pharmacology and disease.Front Pharmacol. 2013 Nov 21;4:144. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2013.00144. eCollection 2013. Front Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24312055 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Acetylation mediates Cx43 reduction caused by electrical stimulation.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015 Oct;87:54-64. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Aug 8. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26264759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold J. M., Phipps M. W., Chen J., Phipps J. (2005). Cellular sublocalization of Cx43 and the establishment of functional coupling in IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells. Mol. Carcinog. 42 159–169 - PubMed
-
- Colussi C., Berni R., Rosati J., Straino S., Vitale S., Spallotta F., et al. (2010). The histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid reduces cardiac arrhythmias in dystrophic mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 87 73–82 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

