γ-Secretase inhibition promotes fibrotic effects of albumin in proximal tubular epithelial cells
- PMID: 23594166
- PMCID: PMC3831705
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12214
γ-Secretase inhibition promotes fibrotic effects of albumin in proximal tubular epithelial cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: Albuminuria is an important biomarker of renal dysfunction and is a major mediator of renal damage and fibrosis during kidney disease. The mechanisms underlying albumin-induced renal fibrosis remain unclear. There has been significant interest in γ-secretase activity in tubular epithelial cells in recent times; however, its potential role in albumin-induced fibrosis has not been investigated.
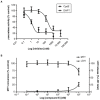
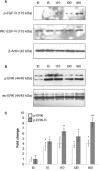
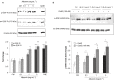
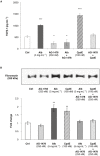
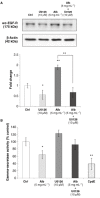
Experimental approach: The primary aim of this study was to examine the role of γ-secretase in albumin-induced fibrotic effects in proximal tubular cells. The effects of increasing albumin concentrations on fibrosis indicators and mediators in the human HK-2 cell line were examined in the presence and absence of a γ-secretase inhibitor, compound E.
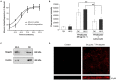
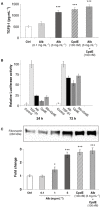
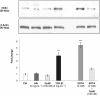
Key results: Treatment with albumin resulted in a number of pro-fibrotic effects, including up-regulation of fibronectin, TGF-β1 and the EGF-R. Interestingly, similar effects were observed in response to treatment with the γ-secretase inhibitor, compound E. Co-treatment of cells with albumin and an EGF-R inhibitor, AG-1478, resulted in significant inhibition of the observed pro-fibrotic effects, suggesting a major role for the EGF-R in albumin-induced fibrotic events. Albumin-induced effects on the EGF-R appeared to be mediated through inhibition of γ-secretase activity and were dependent on ERK-MAPK signalling.
Conclusions and implications: These results provide novel insights into the mechanisms of albumin-induced fibrotic effects in tubular epithelial cells, suggesting important roles for the γ-secretase and the EGF-R. These results suggest that the proposed use of γ-secretase inhibitors as anti-fibrotic agents requires further investigation.
© 2013 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Linking receptor-mediated endocytosis and cell signaling: evidence for regulated intramembrane proteolysis of megalin in proximal tubule.J Biol Chem. 2004 Aug 13;279(33):34302-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405608200. Epub 2004 Jun 4. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15180987
-
Pirfenidone suppresses MAPK signalling pathway to reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis.Nephrology (Carlton). 2017 Aug;22(8):589-597. doi: 10.1111/nep.12831. Nephrology (Carlton). 2017. PMID: 27245114
-
Role of reactive oxygen species in TGF-beta1-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial cells.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Mar;16(3):667-75. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004050425. Epub 2005 Jan 26. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005. PMID: 15677311
-
Metformin attenuates folic-acid induced renal fibrosis in mice.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Sep;233(9):7045-7054. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26505. Epub 2018 Mar 25. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29380373
-
New insights into Notch1 regulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR1 signaling axis: targeted therapy of γ-secretase inhibitor resistant T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cell Signal. 2014 Jan;26(1):149-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.09.021. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24140475 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR/ErbB) for the potential treatment of renal pathologies.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 21;15:1394997. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1394997. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39234105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Participation of the SMAD2/3 signalling pathway in the down regulation of megalin/LRP2 by transforming growth factor beta (TGF-ß1).PLoS One. 2019 May 23;14(5):e0213127. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213127. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31120873 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis in the Proximal Tubule.Annu Rev Physiol. 2017 Feb 10;79:425-448. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034234. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Annu Rev Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27813828 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbate M, Zoja C, Remuzzi G. How does proteinuria cause progressive renal damage? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:2974–2984. - PubMed
-
- Arici M, Brown J, Williams M, Harris KP, Walls J, Brunskill NJ. Fatty acids carried on albumin modulate proximal tubular cell fibronectin production: a role for protein kinase C. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002;17:1751–1757. - PubMed
-
- Baines RJ, Brunskill NJ. The molecular interactions between filtered proteins and proximal tubular cells in proteinuria. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2008;110:e67–e71. - PubMed
-
- Biemesderfer D. Regulated intramembrane proteolysis of megalin: linking urinary protein and gene regulation in proximal tubule? Kidney Int. 2006;69:1717–1721. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

