Adenosine kinase: exploitation for therapeutic gain
- PMID: 23592612
- PMCID: PMC3698936
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.112.006361
Adenosine kinase: exploitation for therapeutic gain
Abstract
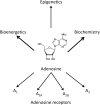
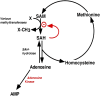
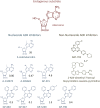
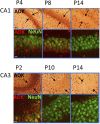
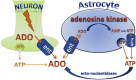
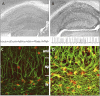
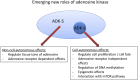
Adenosine kinase (ADK; EC 2.7.1.20) is an evolutionarily conserved phosphotransferase that converts the purine ribonucleoside adenosine into 5'-adenosine-monophosphate. This enzymatic reaction plays a fundamental role in determining the tone of adenosine, which fulfills essential functions as a homeostatic and metabolic regulator in all living systems. Adenosine not only activates specific signaling pathways by activation of four types of adenosine receptors but it is also a primordial metabolite and regulator of biochemical enzyme reactions that couple to bioenergetic and epigenetic functions. By regulating adenosine, ADK can thus be identified as an upstream regulator of complex homeostatic and metabolic networks. Not surprisingly, ADK dysfunction is involved in several pathologies, including diabetes, epilepsy, and cancer. Consequently, ADK emerges as a rational therapeutic target, and adenosine-regulating drugs have been tested extensively. In recent attempts to improve specificity of treatment, localized therapies have been developed to augment adenosine signaling at sites of injury or pathology; those approaches include transplantation of stem cells with deletions of ADK or the use of gene therapy vectors to downregulate ADK expression. More recently, the first human mutations in ADK have been described, and novel findings suggest an unexpected role of ADK in a wider range of pathologies. ADK-regulating strategies thus represent innovative therapeutic opportunities to reconstruct network homeostasis in a multitude of conditions. This review will provide a comprehensive overview of the genetics, biochemistry, and pharmacology of ADK and will then focus on pathologies and therapeutic interventions. Challenges to translate ADK-based therapies into clinical use will be discussed critically.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adenosine kinase: An epigenetic modulator in development and disease.Neurochem Int. 2021 Jul;147:105054. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105054. Epub 2021 May 5. Neurochem Int. 2021. PMID: 33961946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transgenic overexpression of adenosine kinase aggravates cell death in ischemia.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007 Jan;27(1):1-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600334. Epub 2006 May 10. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007. PMID: 16685255
-
Dynamic Regulation of the Adenosine Kinase Gene during Early Postnatal Brain Development and Maturation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2016 Oct 20;9:99. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00099. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27812320 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of Chinese hamster cells mutants affected in adenosine kinase and showing novel genetic and biochemical characteristics.BMC Biochem. 2011 May 17;12:22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2091-12-22. BMC Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21586167 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine kinase: A key regulator of purinergic physiology.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 May;187:114321. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114321. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33161022 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental Role of Adenosine Kinase in the Cerebellum.eNeuro. 2021 Jun 2;8(3):ENEURO.0011-21.2021. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0011-21.2021. Print 2021 May-Jun. eNeuro. 2021. PMID: 33863781 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of ENT1 enhances the impact of specific dietary fats on energy metabolism gene expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Sep 3;121(36):e2321874121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2321874121. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39207736 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic adenosine A₁ receptors modulate excitatory transmission in the rat basolateral amygdala.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Feb;77:465-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.10.029. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24212058 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Adenosine Kinase Attenuates Acute Lung Injury.Crit Care Med. 2016 Apr;44(4):e181-9. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001370. Crit Care Med. 2016. PMID: 26491864 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning-Based Feature Extraction with MRI Data in Neuroimaging Genetics for Alzheimer's Disease.Genes (Basel). 2023 Mar 1;14(3):626. doi: 10.3390/genes14030626. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Brambilla R, Ceruti S, Kim HO, von Lubitz DK, Jacobson KA, Cattabeni F. (1995) G protein-dependent activation of phospholipase C by adenosine A3 receptors in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol 48:1038–1045 - PubMed
-
- Akkari R, Burbiel JC, Hockemeyer J, Müller CE. (2006) Recent progress in the development of adenosine receptor ligands as antiinflammatory drugs. Curr Top Med Chem 6:1375–1399 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
