Attenuating homologous recombination stimulates an AID-induced antileukemic effect
- PMID: 23589568
- PMCID: PMC3646491
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20121258
Attenuating homologous recombination stimulates an AID-induced antileukemic effect
Abstract
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) is critical in normal B cells to initiate somatic hypermutation and immunoglobulin class switch recombination. Accumulating evidence suggests that AID is also prooncogenic, inducing cancer-promoting mutations or chromosome rearrangements. In this context, we find that AID is expressed in >40% of primary human chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cases, consistent with other reports. Using a combination of human B lymphoid leukemia cells and mouse models, we now show that AID expression can be harnessed for antileukemic effect, after inhibition of the RAD51 homologous recombination (HR) factor with 4,4'-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2-2'-disulfonic acid (DIDS). As a proof of principle, we show that DIDS treatment inhibits repair of AID-initiated DNA breaks, induces apoptosis, and promotes cytotoxicity preferentially in AID-expressing human CLL. This reveals a novel antineoplastic role of AID that can be triggered by inhibition of HR, suggesting a potential new paradigm to treat AID-expressing tumors. Given the growing list of tumor types with aberrant AID expression, this novel therapeutic approach has potential to impact a significant patient population.
Figures
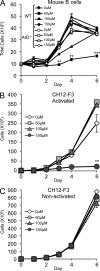
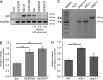
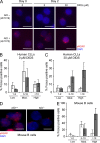
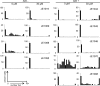
Similar articles
-
Genetic and Small Molecule Disruption of the AID/RAD51 Axis Similarly Protects Nonobese Diabetic Mice from Type 1 Diabetes through Expansion of Regulatory B Lymphocytes.J Immunol. 2017 Jun 1;198(11):4255-4267. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700024. Epub 2017 May 1. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28461573 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the efficacy of glycolytic blockade in cancer cells via RAD51 inhibition.Cancer Biol Ther. 2019;20(2):169-182. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1507666. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Cancer Biol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30183475 Free PMC article.
-
DEK is required for homologous recombination repair of DNA breaks.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 20;7:44662. doi: 10.1038/srep44662. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28317934 Free PMC article.
-
What do somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination teach us about chronic lymphocytic leukaemia pathogenesis?Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;294:71-89. doi: 10.1007/3-540-29933-5_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16323428 Review.
-
Complex regulation and function of activation-induced cytidine deaminase.Trends Immunol. 2011 May;32(5):194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.03.003. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Trends Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21493144 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electrophilic fatty acids impair RAD51 function and potentiate the effects of DNA-damaging agents on growth of triple-negative breast cells.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jan 11;294(2):397-404. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AC118.005899. Epub 2018 Nov 26. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30478172 Free PMC article.
-
Generating and repairing genetically programmed DNA breaks during immunoglobulin class switch recombination.F1000Res. 2018 Apr 13;7:458. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.13247.1. eCollection 2018. F1000Res. 2018. PMID: 29744038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex downstream effects of nuclear export inhibition in B-cell lymphomas: a possible role for activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID).Haematologica. 2013 Sep;98(9):e111-3. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.094540. Haematologica. 2013. PMID: 24006409 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Molecular Determinant of DIDS Analogs Targeting RAD51 Activity.Molecules. 2021 Sep 8;26(18):5460. doi: 10.3390/molecules26185460. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34576930 Free PMC article.
-
Abrogated AID Function Prolongs Survival and Diminishes Renal Pathology in the BXSB Mouse Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.J Immunol. 2020 Mar 1;204(5):1091-1100. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900501. Epub 2020 Jan 27. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31988182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheson B.D., Vena D.A., Barrett J., Freidlin B. 1999. Second malignancies as a consequence of nucleoside analog therapy for chronic lymphoid leukemias. J. Clin. Oncol. 17:2454–2460 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

