Plasma miRNAs as biomarkers to identify patients with castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer
- PMID: 23574937
- PMCID: PMC3645714
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms14047757
Plasma miRNAs as biomarkers to identify patients with castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer
Abstract
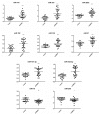
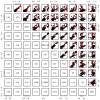
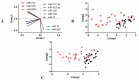
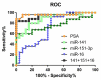
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as key regulators of numerous biological processes, and increasing evidence suggests that circulating miRNAs may be useful biomarkers of clinical disease. In this study, we sought to identify plasma miRNAs that differentiate patients with metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) from those with localized prostate cancer (PCa). Pooled plasma samples from patients with localized PCa or mCRPC (25 per group) were assayed using the Exiqon miRNA qPCR panel, and the differential expression of selected candidates was validated using qRT-PCR. We identified 63 miRNAs upregulated in mCRPC versus localized PCa, while only four were downregulated. Pearson's correlation analysis revealed two highly correlated groups: one consisting of miR-141, miR375 and miR-200c and the other including miR151-3p, miR423-3p, miR-126, miR152 and miR-21. A third group, containing miR-16 and miR-205, showed less correlation. One miRNA from each group (miR-141, miR151-3p and miR-16) was used for logistic regression analysis and proved to increase the sensitivity of the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test alone. While no miRNA alone differentiated localized PCa and mCRPC, combinations had greater sensitivity and specificity. The expression of these 10 candidates was assayed for association with clinical parameters of disease progression through the cBio portal. Our results demonstrate that plasma levels of selected miRNAs are potential biomarkers to differentiate localized PCa and mCRPC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating mRNAs and miRNAs as candidate markers for the diagnosis and prognosis of prostate cancer.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 14;12(9):e0184094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184094. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28910345 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Functional roles and potential clinical application of miRNA-345-5p in prostate cancer.Prostate. 2018 Sep;78(12):927-937. doi: 10.1002/pros.23650. Epub 2018 May 10. Prostate. 2018. PMID: 29748958
-
Expression differences of circulating microRNAs in metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer and low-risk, localized prostate cancer.Prostate. 2013 Mar;73(4):346-54. doi: 10.1002/pros.22572. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Prostate. 2013. PMID: 22887127 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of miR-98-5p, miR-152-3p, miR-326 and miR-4289 Expression as Biomarker for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 6;20(5):1154. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051154. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30845775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of MicroRNA-21 in Prostate Cancer Progression and Metastasis: Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Targets.Ann Surg Oncol. 2024 Jul;31(7):4795-4808. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-15453-z. Epub 2024 May 17. Ann Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38758485 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Stratification of Metastatic Prostate Cancer Patients Treated With Abiraterone and Enzalutamide Through an Integrated Analysis of Circulating Free microRNAs and Clinical Parameters.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 16;11:626104. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.626104. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33796462 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of miR-21 for prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Biosci Rep. 2022 Jan 28;42(1):BSR20211972. doi: 10.1042/BSR20211972. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 34931228 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Prognostic, predictive significance and pathway insights.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 18;19(4):e0296198. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296198. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38635644 Free PMC article.
-
Ago-RIP-Seq identifies Polycomb repressive complex I member CBX7 as a major target of miR-375 in prostate cancer progression.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 13;7(37):59589-59603. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10729. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27449098 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular microRNAs in urologic malignancies: chances and challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jul 16;14(7):14785-99. doi: 10.3390/ijms140714785. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23863690 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A., Siegel R., Ward E., Hao Y., Xu J., Murray T., Thun M.J. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Bartel D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Bushati N., Cohen S.M. microRNA functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007;23:175–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

