Deficiency of ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1 in macrophages increases inflammation and accelerates atherosclerosis in mice
- PMID: 23572498
- PMCID: PMC3839866
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301086
Deficiency of ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1 in macrophages increases inflammation and accelerates atherosclerosis in mice
Abstract
Rationale: Plasma high-density lipoprotein levels are inversely correlated with atherosclerosis. Although it is widely assumed that this is attributable to the ability of high-density lipoprotein to promote cholesterol efflux from macrophage foam cells, direct experimental support for this hypothesis is lacking.
Objective: To assess the role of macrophage cholesterol efflux pathways in atherogenesis.
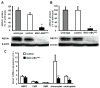
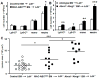
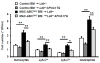
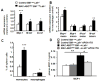
Methods and results: We developed mice with efficient deletion of the ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1 (ABCA1 and ABCG1) in macrophages (MAC-ABC(DKO) mice) but not in hematopoietic stem or progenitor populations. MAC-ABC(DKO) bone marrow (BM) was transplanted into Ldlr(-/-) recipients. On the chow diet, these mice had similar plasma cholesterol and blood monocyte levels but increased atherosclerosis compared with controls. On the Western-type diet, MAC-ABC(DKO) BM-transplanted Ldlr(-/-) mice had disproportionate atherosclerosis, considering they also had lower very low-density lipoprotein/low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels than controls. ABCA1/G1-deficient macrophages in lesions showed increased inflammatory gene expression. Unexpectedly, Western-type diet-fed MAC-ABC(DKO) BM-transplanted Ldlr(-/-) mice displayed monocytosis and neutrophilia in the absence of hematopoietic stem and multipotential progenitor cells proliferation. Mechanistic studies revealed increased expressions of machrophage colony stimulating factor and granulocyte colony stimulating factor in splenic macrophage foam cells, driving BM monocyte and neutrophil production.
Conclusions: These studies show that macrophage deficiency of ABCA1/G1 is proatherogenic likely by promoting plaque inflammation and uncover a novel positive feedback loop in which cholesterol-laden splenic macrophages signal BM progenitors to produce monocytes, with suppression by macrophage cholesterol efflux pathways.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; high-density lipoprotein; inflammation; macrophages; monocytes.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Activation of liver X receptor decreases atherosclerosis in Ldlr⁻/⁻ mice in the absence of ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1 in myeloid cells.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Feb;34(2):279-84. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302781. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24311381 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-3/granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor promotes stem cell expansion, monocytosis, and atheroma macrophage burden in mice with hematopoietic ApoE deficiency.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 May;34(5):976-84. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.303097. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24651678 Free PMC article.
-
Increased inflammatory gene expression in ABC transporter-deficient macrophages: free cholesterol accumulation, increased signaling via toll-like receptors, and neutrophil infiltration of atherosclerotic lesions.Circulation. 2008 Oct 28;118(18):1837-47. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.793869. Epub 2008 Oct 13. Circulation. 2008. PMID: 18852364 Free PMC article.
-
Foam cells in atherosclerosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:245-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jun 16. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23782937 Review.
-
ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1, HDL metabolism, cholesterol efflux, and inflammation: important targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 May;12(5):647-60. doi: 10.2174/138945011795378522. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21039336 Review.
Cited by
-
Bifunctional supramolecular nanofiber inhibits atherosclerosis by enhancing plaque stability and anti-inflammation in apoE-/- mice.Theranostics. 2020 Aug 13;10(22):10231-10244. doi: 10.7150/thno.48410. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32929345 Free PMC article.
-
LXRs link metabolism to inflammation through Abca1-dependent regulation of membrane composition and TLR signaling.Elife. 2015 Jul 14;4:e08009. doi: 10.7554/eLife.08009. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26173179 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid-Specific Deletion of Epsins 1 and 2 Reduces Atherosclerosis by Preventing LRP-1 Downregulation.Circ Res. 2019 Feb 15;124(4):e6-e19. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313028. Circ Res. 2019. PMID: 30595089 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Gene Expression in Macrophages From Human Atherosclerotic Plaques Shows Convergence on Pathways Implicated by Genome-Wide Association Study Risk Variants.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Nov;38(11):2718-2730. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311209. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 30354237 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol Suppresses Proinflammatory Cytokine Production by Increasing ABCA1 Expression via Mediation by the Long Noncoding RNA LOC286367.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Dec 17;2018:8907143. doi: 10.1155/2018/8907143. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 30647536 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gordon T, Castelli WP, Hjortland MC, Kannel WB, Dawber TR. High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. The framingham study. Am J Med. 1977;62:707–714. - PubMed
-
- Barter PJ, Caulfield M, Eriksson M, Grundy SM, Kastelein JJ, Komajda M, Lopez-Sendon J, Mosca L, Tardif JC, Waters DD, Shear CL, Revkin JH, Buhr KA, Fisher MR, Tall AR, Brewer B, Investigators I. Effects of torcetrapib in patients at high risk for coronary events. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2109–2122. - PubMed
-
- Investigators AH, Boden WE, Probstfield JL, Anderson T, Chaitman BR, Desvignes-Nickens P, Koprowicz K, McBride R, Teo K, Weintraub W. Niacin in patients with low hdl cholesterol levels receiving intensive statin therapy. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2255–2267. - PubMed
-
- Tardif JC, Gregoire J, L’Allier PL, Ibrahim R, Lesperance J, Heinonen TM, Kouz S, Berry C, Basser R, Lavoie MA, Guertin MC, Rodes-Cabau J. Effect of r HDLoA-S, Efficacy I. Effects of reconstituted high-density lipoprotein infusions on coronary atherosclerosis: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2007;297:1675–1682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

