Word list learning in patients with polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy
- PMID: 23569454
- PMCID: PMC3618099
- DOI: 10.1159/000346857
Word list learning in patients with polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy
Abstract
Background/aims: Polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy (PLOSL) is a rare hereditary disease that is characterized by a combination of progressive presenile dementia and sclerosing leukoencephalopathy with bone cysts. No quantitative information on verbal memory functioning in PLOSL patients compared with control subjects is available.
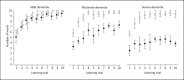
Methods: 23 patients with PLOSL and 23 control subjects were examined with a version of the 10-word list-learning task. Learning curves were compared between the patients and the matched control subjects.
Results: Compared with the control subjects, PLOSL patients with moderate or severe dementia were impaired in both learning trials and delayed recall on the 10-word list-learning test.
Conclusion: Progressive degeneration of brain structures affecting the hippocampus and the medial temporal lobe with advanced PLOSL disease contributes to an inefficient verbal learning process.
Keywords: Dementia; Frontal lobe degeneration; Nasu-Hakola disease; Polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polycystic Lipomembranous Osteodysplasia with Sclerosing Leukoencephalopathy (PLOSL): a new report of an Italian woman and review of the literature.J Neurol Sci. 2013 Mar 15;326(1-2):115-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.01.021. Epub 2013 Feb 9. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23399524 Review.
-
Nasu-Hakola disease (polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy--PLOSL): a dementia associated with bone cystic lesions. From clinical to genetic and molecular aspects.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2004 Feb;24(1):1-24. doi: 10.1023/b:cemn.0000012721.08168.ee. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2004. PMID: 15049507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early-onset dementia, leukoencephalopathy and brain calcifications: a clinical, imaging and pathological comparison of ALSP and PLOSL/Nasu Hakola disease.Acta Neurol Belg. 2018 Dec;118(4):607-615. doi: 10.1007/s13760-018-1023-8. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Acta Neurol Belg. 2018. PMID: 30242731
-
CNS manifestations of Nasu-Hakola disease: a frontal dementia with bone cysts.Neurology. 2001 Jun 12;56(11):1552-8. doi: 10.1212/wnl.56.11.1552. Neurology. 2001. PMID: 11402114
-
Extremity manifestations and surgical treatment for nasu hakola disease.Case Rep Orthop. 2014;2014:458728. doi: 10.1155/2014/458728. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Case Rep Orthop. 2014. PMID: 24711942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hakola HP. Neuropsychiatric and genetic aspects of a new hereditary disease characterized by progressive dementia and lipomembranous polycystic osteodysplasia. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1972;232:1–173. - PubMed
-
- Nasu T, Tsukahara Y, Terayama K. A libid metabolic disease – ‘membranous lipodystrophy’. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1973;23:539–558. - PubMed
-
- Paloneva J, Autti T, Raininko R, Partanen J, Salonen O, Puranen M, Hakola P, Haltia M. CNS manifestations of Nasu-Hakola disease: a frontal dementia with bone cysts. Neurology. 2001;56:1552–1558. - PubMed
-
- Hakola HP. Polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy (membranous lipodystrophy): a neuropsychiatric follow-up study. Monogr Psychiatr Fenn. 1990;17:1–114.
-
- Pekkarinen P, Kestilä M, Paloneva J, Terwilliger J, Varilo T, Järvi O, Hakola P, Peltonen L. Fine-scale mapping of a novel dementia gene, PLOSL, by linkage disequilibrium. Genomics. 1998;54:307–315. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources