Leptin, diabetes, and the brain
- PMID: 23565487
- PMCID: PMC3602981
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-8210.105568
Leptin, diabetes, and the brain
Abstract
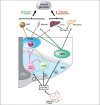
Diabetes is a major worldwide problem. Despite some progress in the development of new antidiabetic agents, the ability to maintain tight glycemic control in order to prevent renal, retinal, and neuropathic complications of diabetes without adverse complications still remains a challenge. Recent evidence suggests, however, that in addition to playing a key role in the regulation of energy homeostasis, the adiposity hormone leptin also plays an important role in the control of glucose metabolism via its actions in the brain. This review examines the role of leptin action in the central nervous system and the mechanisms whereby leptin mediates its effects to regulate glucose metabolism. These findings suggest that defects or dysfunction in leptin signaling may contribute to the etiology of diabetes and raise the possibility that either leptin or downstream targets of leptin may have therapeutic potential for the treatment of diabetes.
Keywords: Brain; diabetes; glucose; insulin; leptin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
CNS Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis: Role of the Leptin-Melanocortin System.Curr Diab Rep. 2020 May 26;20(7):29. doi: 10.1007/s11892-020-01311-1. Curr Diab Rep. 2020. PMID: 32451760 Review.
-
The role of leptin in diabetes: metabolic effects.Diabetologia. 2016 May;59(5):928-32. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-3898-3. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 26969486 Review.
-
Leptin signaling regulates glucose homeostasis, but not adipostasis, in the zebrafish.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Mar 15;113(11):3084-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1513212113. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26903647 Free PMC article.
-
Rethinking leptin and insulin action: therapeutic opportunities for diabetes.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38(5-6):820-30. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.09.013. Epub 2005 Oct 3. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16236542 Review.
-
Leptin and the central nervous system control of glucose metabolism.Physiol Rev. 2011 Apr;91(2):389-411. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00007.2010. Physiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21527729 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adiposity, related biomarkers, and type 2 diabetes after gestational diabetes: The Diabetes Prevention Program.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022 Jan;30(1):221-228. doi: 10.1002/oby.23291. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022. PMID: 34796678 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of Leptin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Cureus. 2024 Apr 5;16(4):e57667. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57667. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38707092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ErbB4 deletion predisposes to development of metabolic syndrome in mice.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Oct 1;315(4):E583-E593. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00166.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 29944391 Free PMC article.
-
The functional state of hormone-sensitive adenylyl cyclase signaling system in diabetes mellitus.J Signal Transduct. 2013;2013:594213. doi: 10.1155/2013/594213. Epub 2013 Sep 28. J Signal Transduct. 2013. PMID: 24191197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leptin concentrations in type 2 diabetes and non-diabetes Nigerian-Africans.Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Oct 15;10(4):444-454. eCollection 2020. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 33224595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smyth S, Heron A. Diabetes and obesity: The twin epidemics. Nat Med. 2006;12:75–80. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Magliano DJ, Zimmet PZ. The worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus-present and future perspectives. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;8:228–36. - PubMed
-
- Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. in 2007. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:596–615. - PubMed
-
- Kahn SE, Prigeon RL, McCulloch DK, Boyko EJ, Bergman RN, Schwartz MW, et al. Quantification of the relationship between insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function in human subjects.Evidence for a hyperbolic function. Diabetes. 1993;42:1663–72. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
