Genomic regions flanking E-box binding sites influence DNA binding specificity of bHLH transcription factors through DNA shape
- PMID: 23562153
- PMCID: PMC3640701
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.03.014
Genomic regions flanking E-box binding sites influence DNA binding specificity of bHLH transcription factors through DNA shape
Abstract
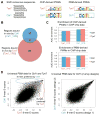
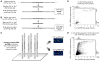
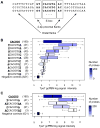
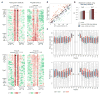
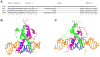
DNA sequence is a major determinant of the binding specificity of transcription factors (TFs) for their genomic targets. However, eukaryotic cells often express, at the same time, TFs with highly similar DNA binding motifs but distinct in vivo targets. Currently, it is not well understood how TFs with seemingly identical DNA motifs achieve unique specificities in vivo. Here, we used custom protein-binding microarrays to analyze TF specificity for putative binding sites in their genomic sequence context. Using yeast TFs Cbf1 and Tye7 as our case studies, we found that binding sites of these bHLH TFs (i.e., E-boxes) are bound differently in vitro and in vivo, depending on their genomic context. Computational analyses suggest that nucleotides outside E-box binding sites contribute to specificity by influencing the three-dimensional structure of DNA binding sites. Thus, the local shape of target sites might play a widespread role in achieving regulatory specificity within TF families.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
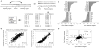

Similar articles
-
Curated collection of yeast transcription factor DNA binding specificity data reveals novel structural and gene regulatory insights.Genome Biol. 2011 Dec 21;12(12):R125. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-12-r125. Genome Biol. 2011. PMID: 22189060 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive, high-resolution binding energy landscapes reveal context dependencies of transcription factor binding.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Apr 17;115(16):E3702-E3711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1715888115. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29588420 Free PMC article.
-
Non-DNA-binding cofactors enhance DNA-binding specificity of a transcriptional regulatory complex.Mol Syst Biol. 2011 Dec 6;7:555. doi: 10.1038/msb.2011.89. Mol Syst Biol. 2011. PMID: 22146299 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved role for transcription factor sumoylation in binding-site selection.Curr Genet. 2019 Dec;65(6):1307-1312. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00992-w. Epub 2019 May 15. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 31093693 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Binding Specificity among bHLH Transcription Factors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 24;22(17):9150. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179150. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502060 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bayesian Markov models consistently outperform PWMs at predicting motifs in nucleotide sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 27;44(13):6055-69. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw521. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27288444 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into protein-DNA binding specificity from hydrogen bond based comparative study.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Dec 2;47(21):11103-11113. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz963. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31665426 Free PMC article.
-
Coregulation of transcription factor binding and nucleosome occupancy through DNA features of mammalian enhancers.Mol Cell. 2014 Jun 5;54(5):844-857. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.04.006. Epub 2014 May 8. Mol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24813947 Free PMC article.
-
A natural mutation in the promoter of the aconitase gene ZjACO3 influences fruit citric acid content in jujube.Hortic Res. 2024 Jan 3;11(3):uhae003. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhae003. eCollection 2024 Mar. Hortic Res. 2024. PMID: 38464475 Free PMC article.
-
SELMAP - SELEX affinity landscape MAPping of transcription factor binding sites using integrated microfluidics.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 15;6:33351. doi: 10.1038/srep33351. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27628341 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

