Insulin-receptor substrate-2 (irs-2) is required for maintaining glucokinase and glucokinase regulatory protein expression in mouse liver
- PMID: 23560040
- PMCID: PMC3613347
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058797
Insulin-receptor substrate-2 (irs-2) is required for maintaining glucokinase and glucokinase regulatory protein expression in mouse liver
Abstract
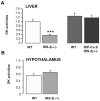
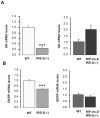
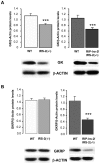
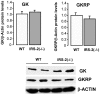
Insulin receptor substrate (IRS) proteins play important roles in hepatic nutrient homeostasis. Since glucokinase (GK) and glucokinase regulatory protein (GKRP) function as key glucose sensors, we have investigated the expression of GK and GKRP in liver of Irs-2 deficient mice and Irs2(-/-) mice where Irs2 was reintroduced specifically into pancreatic β-cells [RIP-Irs-2/IRS-2(-/-)]. We observed that liver GK activity was significantly lower (p<0.0001) in IRS-2(-/-) mice. However, in RIP-Irs-2/IRS-2(-/-) mice, GK activity was similar to the values observed in wild-type animals. GK activity in hypothalamus was not altered in IRS-2(-/-) mice. GK and GKRP mRNA levels in liver of IRS-2(-/-) were significantly lower, whereas in RIP-Irs-2/IRS-2(-/-) mice, both GK and GKRP mRNAs levels were comparable to wild-type animals. At the protein level, the liver content of GK was reduced in IRS-2(-/-) mice as compared with controls, although GKRP levels were similar between these experimental models. Both GK and GKRP levels were lower in RIP-Irs-2/IRS-2(-/-) mice. These results suggest that IRS-2 signalling is important for maintaining the activity of liver GK. Moreover, the differences between liver and brain GK may be explained by the fact that expression of hepatic, but not brain, GK is controlled by insulin. GK activity was restored by the β-cell compensation in the RIP-Irs-2/IRS-2 mice. Interestingly, GK and GKRP protein expression remained low in RIP-Irs-2/IRS-2(-/-) mice, perhaps reflecting different mRNA half-lives or alterations in the process of translation and post-translational regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mice mutant for glucokinase regulatory protein exhibit decreased liver glucokinase: a sequestration mechanism in metabolic regulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Dec 7;96(25):14511-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14511. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10588736 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylation of glucokinase regulatory protein decreases glucose metabolism by suppressing glucokinase activity.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 1;5:17395. doi: 10.1038/srep17395. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26620281 Free PMC article.
-
An allosteric activator of glucokinase impairs the interaction of glucokinase and glucokinase regulatory protein and regulates glucose metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2006 Dec 8;281(49):37668-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605186200. Epub 2006 Oct 6. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 17028192
-
Recent Updates on Glucokinase Activators and Glucokinase Regulatory Protein Disrupters for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019;15(3):205-212. doi: 10.2174/1573399814666180724100749. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019. PMID: 30039763 Review.
-
Hormonal and Metabolite Regulation of Hepatic Glucokinase.Annu Rev Nutr. 2016 Jul 17;36:389-415. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071715-051145. Epub 2016 May 4. Annu Rev Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27146014 Review.
Cited by
-
Progesterone-Regulated Endometrial Factors Controlling Implantation.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2016 Mar;75(3):237-45. doi: 10.1111/aji.12473. Epub 2016 Jan 24. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26804062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Chemical Constituents from Fruits of Catalpa bignonioides Walt. and Their α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity and Insulin Secretion Effect.Molecules. 2021 Jan 12;26(2):362. doi: 10.3390/molecules26020362. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33445612 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of progesterone receptor A and B isoforms during human endometrial decidualization.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Jun;29(6):882-95. doi: 10.1210/me.2014-1363. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25875046 Free PMC article.
-
Liraglutide ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in diabetic mice via the IRS2/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019 Jul 4;12:1013-1021. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S206867. eCollection 2019. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019. PMID: 31308717 Free PMC article.
-
Gymnema Sylvestre Supplementation Restores Normoglycemia, Corrects Dyslipidemia, and Transcriptionally Modulates Pancreatic and Hepatic Gene Expression in Alloxan-Induced Hyperglycemic Rats.Metabolites. 2023 Apr 4;13(4):516. doi: 10.3390/metabo13040516. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37110174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersson U, Filipsson K, Abbott CR, Woods A, Smith K, et al. (2004) AMP-activated protein kinase plays a role in the control of food intake. J Biol Chem 279: 12005–12008. - PubMed
-
- Rother KI, Imai Y, Caruso M, Beguinot F, Formisano P, et al. (1998) Evidence that IRS-2 phosphorylation is required for insulin action in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 273: 17491–17497. - PubMed
-
- Valverde AM, Burks DJ, Fabregat I, Fisher TL, Carretero J, et al. (2003) Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance in IRS-2-deficient hepatocytes. Diabetes 52: 2239–2248. - PubMed
-
- Valverde AM, Fabregat I, Burks DJ, White MF, Benito M (2004) IRS-2 mediates the antiapoptotic effect of insulin in neonatal hepatocytes. Hepatology 40: 1285–1294. - PubMed
-
- Kubota N, Tobe K, Terauchi Y, Eto K, Yamauchi T, et al. (2000) Disruption of insulin receptor substrate 2 causes type 2 diabetes because of liver insulin resistance and lack of compensatory beta-cell hyperplasia. Diabetes 49: 1880–1889. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

