The Smc5/Smc6/MAGE complex confers resistance to caffeine and genotoxic stress in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 23555814
- PMCID: PMC3610895
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059866
The Smc5/Smc6/MAGE complex confers resistance to caffeine and genotoxic stress in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
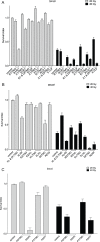
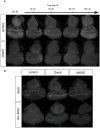
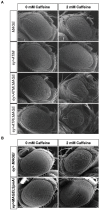
The SMC5/6 protein complex consists of the Smc5, Smc6 and Non-Smc-Element (Nse) proteins and is important for genome stability in many species. To identify novel components in the DNA repair pathway, we carried out a genetic screen to identify mutations that confer reduced resistance to the genotoxic effects of caffeine, which inhibits the ATM and ATR DNA damage response proteins. This approach identified inactivating mutations in CG5524 and MAGE, homologs of genes encoding Smc6 and Nse3 in yeasts. The fact that Smc5 mutants are also caffeine-sensitive and that Mage physically interacts with Drosophila homologs of Nse proteins suggests that the structure of the Smc5/6 complex is conserved in Drosophila. Although Smc5/6 proteins are required for viability in S. cerevisiae, they are not essential under normal circumstances in Drosophila. However, flies carrying mutations in Smc5, Smc6 and MAGE are hypersensitive to genotoxic agents such as ionizing radiation, camptothecin, hydroxyurea and MMS, consistent with the Smc5/6 complex serving a conserved role in genome stability. We also show that mutant flies are not compromised for pre-mitotic cell cycle checkpoint responses. Rather, caffeine-induced apoptosis in these mutants is exacerbated by inhibition of ATM or ATR checkpoint kinases but suppressed by Rad51 depletion, suggesting a functional interaction involving homologous DNA repair pathways that deserves further scrutiny. Our insights into the SMC5/6 complex provide new challenges for understanding the role of this enigmatic chromatin factor in multi-cellular organisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nse1, Nse2, and a novel subunit of the Smc5-Smc6 complex, Nse3, play a crucial role in meiosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Nov;15(11):4866-76. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-05-0436. Epub 2004 Aug 25. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15331764 Free PMC article.
-
SMC5 and SMC6 genes are required for the segregation of repetitive chromosome regions.Nat Cell Biol. 2005 Apr;7(4):412-9. doi: 10.1038/ncb1239. Epub 2005 Mar 27. Nat Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15793567
-
The Smc5-Smc6 DNA repair complex. bridging of the Smc5-Smc6 heads by the KLEISIN, Nse4, and non-Kleisin subunits.J Biol Chem. 2006 Dec 1;281(48):36952-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608004200. Epub 2006 Sep 27. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 17005570
-
The unnamed complex: what do we know about Smc5-Smc6?Chromosome Res. 2009;17(2):251-63. doi: 10.1007/s10577-008-9016-8. Chromosome Res. 2009. PMID: 19308705 Review.
-
Cohesin, gene expression and development: lessons from Drosophila.Chromosome Res. 2009;17(2):185-200. doi: 10.1007/s10577-009-9022-5. Chromosome Res. 2009. PMID: 19308700 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ecdysteroid kinase-like (EcKL) paralogs confer developmental tolerance to caffeine in Drosophila melanogaster.Curr Res Insect Sci. 2022 Jan 16;2:100030. doi: 10.1016/j.cris.2022.100030. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Insect Sci. 2022. PMID: 36003262 Free PMC article.
-
Necdin: A purposive integrator of molecular interaction networks for mammalian neuron vitality.Genes Cells. 2021 Sep;26(9):641-683. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12884. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Genes Cells. 2021. PMID: 34338396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic sleep loss disrupts rhythmic gene expression in Drosophila.Front Physiol. 2022 Nov 18;13:1048751. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1048751. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36467698 Free PMC article.
-
Early development of Drosophila embryos requires Smc5/6 function during oogenesis.Biol Open. 2016 Jul 15;5(7):928-41. doi: 10.1242/bio.019000. Biol Open. 2016. PMID: 27288507 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Loci Contributing to Natural Variation in Xenobiotic Resistance in Drosophila.PLoS Genet. 2015 Nov 30;11(11):e1005663. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005663. eCollection 2015 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26619284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lehmann AR (2005) The role of SMC proteins in the responses to DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst) 4: 309–314. - PubMed
-
- Hirano T (2006) At the heart of the chromosome: SMC proteins in action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7: 311–322. - PubMed
-
- Cuylen S, Haering CH (2011) Deciphering condensin action during chromosome segregation. Trends Cell Biol 21: 552–559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

