MicroRNA-276a functions in ellipsoid body and mushroom body neurons for naive and conditioned olfactory avoidance in Drosophila
- PMID: 23536094
- PMCID: PMC3640307
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4004-12.2013
MicroRNA-276a functions in ellipsoid body and mushroom body neurons for naive and conditioned olfactory avoidance in Drosophila
Abstract
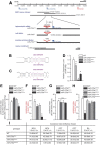
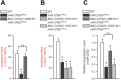
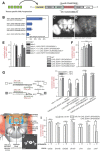
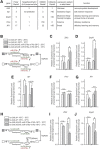
MicroRNA (miRNA)-mediated gene regulation plays a key role in brain development and function. But there are few cases in which the roles of individual miRNAs have been elucidated in behaving animals. We report a miR-276a::DopR regulatory module in Drosophila that functions in distinct circuits for naive odor responses and conditioned odor memory. Drosophila olfactory aversive memory involves convergence of the odors (conditioned stimulus) and the electric shock (unconditioned stimulus) in mushroom body (MB) neurons. Dopamine receptor DopR mediates the unconditioned stimulus inputs onto MB. Distinct dopaminergic neurons also innervate ellipsoid body (EB), where DopR function modulates arousal to external stimuli. We demonstrate that miR-276a is required in MB neurons for memory formation and in EB for naive responses to odors. Both roles of miR-276a are mediated by tuning DopR expression. The dual role of this miR-276a::DopR genetic module in these two neural circuits highlights the importance of miRNA-mediated gene regulation within distinct circuits underlying both naive behavioral responses and memory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mushroom body efferent neurons responsible for aversive olfactory memory retrieval in Drosophila.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Jun 19;14(7):903-10. doi: 10.1038/nn.2846. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21685917
-
Distinct neuronal circuits mediate experience-dependent, non-associative osmotactic responses in Drosophila.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2007 Mar;34(3):378-89. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2006.11.011. Epub 2007 Jan 2. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17197197
-
Dopamine is required for learning and forgetting in Drosophila.Neuron. 2012 May 10;74(3):530-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.04.007. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 22578504 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory learning in Drosophila.Physiology (Bethesda). 2010 Dec;25(6):338-46. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00026.2010. Physiology (Bethesda). 2010. PMID: 21186278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A non-canonical on-demand dopaminergic transmission underlying olfactory aversive learning.Neurosci Res. 2022 May;178:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2021.12.008. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Neurosci Res. 2022. PMID: 34973292 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of miRNAs in Drosophila melanogaster Male Courtship Behavior.Genetics. 2019 Mar;211(3):925-942. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301901. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 30683757 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA Helicase BELLE Is Involved in Circadian Rhythmicity and in Transposons Regulation in Drosophila melanogaster.Front Physiol. 2019 Feb 20;10:133. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00133. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30842743 Free PMC article.
-
Infections of virulent and avirulent viruses differentially influenced the expression of dicer-1, ago-1, and microRNAs in Bombus terrestris.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 4;7:45620. doi: 10.1038/srep45620. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28374846 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the microRNA landscape of Rhodnius prolixus, a vector of Chagas disease.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 12;13(1):13120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40353-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37573416 Free PMC article.
-
Regulators of Long-Term Memory Revealed by Mushroom Body-Specific Gene Expression Profiling in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2018 Aug;209(4):1167-1181. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301106. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29925565 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
