Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling is involved in mitomycin C (MMC)-induced apoptosis in human fibroblasts via PERK pathway
- PMID: 23533616
- PMCID: PMC3606443
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059330
Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling is involved in mitomycin C (MMC)-induced apoptosis in human fibroblasts via PERK pathway
Abstract
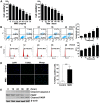
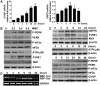
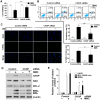
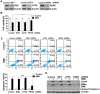
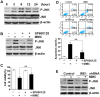
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-mediated cell apoptosis has been implicated in various cell types, including fibroblasts. Previous studies have shown that mitomycin C (MMC)-induced apoptosis occurs in fibroblasts, but the effects of MMC on ER stress-mediated apoptosis in fibroblasts have not been examined. Here, MMC-induced apoptosis in human primary fibroblasts was investigated by exposing cells to a single dose of MMC for 5 minutes. Significant inhibition of cell proliferation and increased apoptosis were observed using a cell viability assay, Annexin V/propidium iodide double staining, cell cycle analysis, and TUNEL (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling) staining. Upregulation of proapoptotic factors, including cleaved caspase-3 and poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP), was detected by Western blotting. MMC-induced apoptosis was correlated with elevation of 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78) and C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), which are hallmarks of ER stress. Three unfolded protein response (UPR) sensors (inositol-requiring enzyme 1, IRE1; activating transcription factor 6, ATF6; and PKR-like ER kinase, PERK) and their downstream signaling pathways were also activated. Knockdown of CHOP attenuated MMC-induced apoptosis by increasing the ratio of BCL-2/BAX and decreasing BIM expression, suggesting that ER stress is involved in MMC-induced fibroblast apoptosis. Interestingly, knockdown of PERK significantly decreased ER stress-mediated apoptosis by reducing the expression of CHOP, BIM and cleaved caspase-3. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging also decreased the expression of GRP78, phospho-PERK, CHOP, and BIM. These results demonstrate that MMC-induced apoptosis is triggered by ROS generation and PERK activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) signaling pathway plays a major role in reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013 Nov 2;12:158. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-158. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013. PMID: 24180212 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of the induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress by the anti-cancer agent, di-2-pyridylketone 4,4-dimethyl-3-thiosemicarbazone (Dp44mT): Activation of PERK/eIF2α, IRE1α, ATF6 and calmodulin kinase.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Jun 1;109:27-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27059255
-
Prodigiosin activates endoplasmic reticulum stress cell death pathway in human breast carcinoma cell lines.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012 Dec 15;265(3):325-34. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2012.08.034. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22982536
-
Molecular signal networks and regulating mechanisms of the unfolded protein response.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017 Jan.;18(1):1-14. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1600043. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017. PMID: 28070992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Basis of Human Diseases and Targeted Therapy Based on Small-Molecule Inhibitors of ER Stress-Induced Signaling Pathways.Curr Mol Med. 2017;17(2):118-132. doi: 10.2174/1566524017666170306122643. Curr Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28266275 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of cardiac fibroblast cell death by unfolded protein response signaling.Front Physiol. 2024 Jan 12;14:1304669. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1304669. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38283278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artesunate prevents knee intraarticular adhesion via PRKR-like ER kinase (PERK) signal pathway.J Orthop Surg Res. 2019 Dec 17;14(1):448. doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1445-x. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31847860 Free PMC article.
-
Homocysteine Induces Apoptosis of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells via Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:5736506. doi: 10.1155/2017/5736506. Epub 2017 May 28. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28630659 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the integrated stress response in ophthalmology.Curr Eye Res. 2021 Aug;46(8):1075-1088. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2020.1867748. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Curr Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 33474991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The clinical significance and function of miR-146 in the promotion of epidural fibrosis.Genet Mol Biol. 2021 May 14;44(2):e20200447. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2020-0447. eCollection 2021. Genet Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33999095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldrete JA (1995) Epidural fibrosis after permanent catheter insertion and infusion. J Pain Symptom Manage 10: 624–631. - PubMed
-
- Cauchoix J, Ficat C, Girard B (1978) Repeat surgery after disc excision. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 3: 256–259. - PubMed
-
- Guyer RD, Patterson M, Ohnmeiss DD (2006) Failed back surgery syndrome: diagnostic evaluation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 14: 534–543. - PubMed
-
- Chandler K, Cappello R (2006) Laminectomy membrane formation in dogs: is the answer still elusive? Vet J 172: 1–2. - PubMed
-
- Jou IM, Tai TW, Tsai CL, Tsai TM, Yung WS, et al. (2007) Spinal somatosensory evoked potential to evaluate neurophysiologic changes associated with postlaminotomy fibrosis: an experimental study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 32: 2111–2118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

