Germline deletion of β2 microglobulin or CD1d reduces anti-phospholipid antibody, but increases autoantibodies against non-phospholipid antigens in the NZB/W F1 model of lupus
- PMID: 23531237
- PMCID: PMC3672782
- DOI: 10.1186/ar4206
Germline deletion of β2 microglobulin or CD1d reduces anti-phospholipid antibody, but increases autoantibodies against non-phospholipid antigens in the NZB/W F1 model of lupus
Abstract
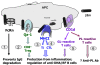
Introduction: β2-microglobulin (β2m) is required for the surface expression of MHC class I and class I-like proteins such as CD1d, Qa1 and neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), all of which may impact the development of autoimmunity. Since CD1d is known to bind and present phospholipid antigens to T cells, we asked if the deficiency of β2m or CD1d will impact the development of anti-phospholipid antibodies as compared to other aspects of lupus autoimmunity.
Methods: We introgressed the β2m-null genotype onto the NZB and NZW backgrounds for 12 to 14 generations to generate genetically lupus-susceptible (NZB/NZW)F1 (BWF1) mice that are β2m-deficient (β2m°). Circulating immunoglobulins (Ig), rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-DNA and anti-cardiolipin (anti-CL) antibodies, and renal disease were analyzed in these and CD1d-deficient (CD1d°) BWF1 mice that we had previously generated.
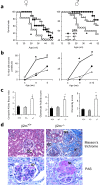
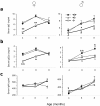
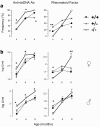
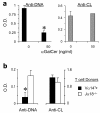
Results: Whereas β2m° BWF1 mice had reduced serum IgG, they had increased mortality, nephritis, serum IgG anti-DNA antibody and RF as compared to heterozygous and wild-type littermates. These effects were recapitulated in CD1d° BWF1 mice, except that they also had increased serum IgG as compared to control littermates. Intriguingly, both β2m° and CD1d° mice had lower serum anti-CL antibody levels than in control littermates. Such CD1d dependence of anti-CL antibody production is not mediated by CD1d/glycolipid-reactive iNKT cells, as these cells reduced the production of RF and anti-DNA antibodies but had no effect on anti-CL antibodies.
Conclusions: We report a novel dichotomous role of β2m and CD1d, whereby these molecules differently regulate autoimmunity against phospholipid versus non-phospholipid autoantigens.
Figures
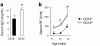
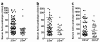
Similar articles
-
Examining the role of CD1d and natural killer T cells in the development of nephritis in a genetically susceptible lupus model.Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Apr;56(4):1219-33. doi: 10.1002/art.22490. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 17393451 Free PMC article.
-
Disparate effects of depletion of CD1d-reactive T cells during early versus late stages of disease in a genetically susceptible model of lupus.Lupus. 2012 Apr;21(5):485-90. doi: 10.1177/0961203311428459. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Lupus. 2012. PMID: 22065098 Free PMC article.
-
Differences between CD8+ T cells in lupus-prone (NZB x NZW) F1 mice and healthy (BALB/c x NZW) F1 mice may influence autoimmunity in the lupus model.Eur J Immunol. 2004 Sep;34(9):2489-99. doi: 10.1002/eji.200424978. Eur J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15307181 Free PMC article.
-
Role of invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells in systemic lupus erythematosus.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(18):1778-87. doi: 10.2174/092986708785132988. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18691038 Review.
-
Anti-phospholipid autoantibodies in human diseases.Clin Immunol. 2023 Nov;256:109803. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2023.109803. Epub 2023 Oct 19. Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37821073 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of mitochondria in rheumatic diseases.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022 Nov;18(11):621-640. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00834-z. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 36175664 Review.
-
"Ways in which the neonatal Fc-receptor is involved in autoimmunity".J Transl Autoimmun. 2021 Sep 11;4:100122. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100122. eCollection 2021. J Transl Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 34568803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The NZB/W F1 mouse model for Sjögren's syndrome: A historical perspective and lessons learned.Autoimmun Rev. 2020 Dec;19(12):102686. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102686. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Autoimmun Rev. 2020. PMID: 33131691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment with anti-neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) antibody ameliorates experimental epidermolysis bullosa acquisita in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 May;177(10):2381-2392. doi: 10.1111/bph.14986. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31975370 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated CD25 and Cytokine Expression by γδ T Cells of Systemic Sclerosis Patients Stimulated With Cardiolipin and Zoledronate.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 13;9:753. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00753. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29706966 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shivakumar S, Tsokos GC, Datta SK. T cell receptor α/β expressing double-negative (CD4-/CD8-) and CD4+ T helper cells in humans augment the production of pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibodies associated with lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 1989;143:103–112. - PubMed
-
- Peng SL, Madaio MP, Hayday AC, Craft J. Propagation and regulation of systemic autoimmunity by gammadelta T cells. J Immunol. 1996;157:5689–5698. - PubMed
-
- Singh RR, Ebling FM, Albuquerque DA, Saxena V, Kumar V, Giannini EH, Marion TN, Finkelman FD, Hahn BH. Induction of autoantibody production is limited in nonautoimmune mice. J Immunol. 2002;169:587–594. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

