Protective effect of edaravone for tourniquet-induced ischemia-reperfusion injury on skeletal muscle in murine hindlimb
- PMID: 23530927
- PMCID: PMC3614524
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-14-113
Protective effect of edaravone for tourniquet-induced ischemia-reperfusion injury on skeletal muscle in murine hindlimb
Abstract
Background: Studies have shown that ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) produces free radicals leading to lipid peroxidation and damage to skeletal muscle. The purposes of this study were 1) to assess the histological findings of gastrocnemius muscle (GC) and tibialis anterior muscle (TA) in I/R injury model mice, 2) to histologically analyze whether a single pretreatment of edaravone inhibits I/R injury to skeletal muscle in murine models and 3) to evaluate the effect of oxidative stress on these muscles.
Methods: C57BL6 mice were divided in two groups, with one group receiving 3 mg/kg intraperitoneal injections of edaravone (I/R + Ed group) and the other group receiving an identical amount of saline (I/R group) 30 minutes before ischemia. Edaravone (3-methy-1-pheny1-2-pyrazolin-5-one) is a potent and novel synthetic scavenger of free radicals. This drug inhibits both nonenzymatic lipid peroxidation and the lipoxygenase pathway, in addition to having potent antioxidant effects against ischemia reperfusion. The duration of the ischemia was 1.5 hours, with reperfusion at either 24 or 72 hours (3 days). Specimens of gastrocnemius (GC) and anterior tibialis (TA) were removed for histological evaluation and biochemical analysis.
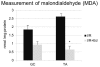
Results: This model of I/R injury was highly reproducible in histologic muscle damage. In the histologic damage score, the mean muscle fibers and inflammatory cell infiltration in the I/R + Ed group were significantly less than the corresponding values of observed in the I/R group. Thus, pretreatment with edaravone was observed to have a protective effect on muscle damage after a period of I/R in mice. In addition, the mean muscle injury score in the I/R + Ed group was also significantly less than the I/R group. In the I/R + Ed group, the mean malondialdehyde (MDA) level was lower than in the I/R group and western-blotting revealed that edaravone pretreatment decreased the level of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression.
Conclusions: Edaravone was found to have a protective effect against I/R injury by directly inhibiting lipid peroxidation of the myocyte by free radicals in skeletal muscles and may also reduce the secondary edema and inflammatory infiltration incidence of oxidative stress on tissue.
Figures

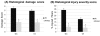
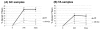

Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effect of edaravone on systemic inflammation and local damage in skeletal muscles following long-term ischemia to murine hind limb.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019 Sep-Dec;27(3):2309499019874470. doi: 10.1177/2309499019874470. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019. PMID: 31549573
-
Antioxidant effect of MCI-186, a new Free-Radical scavenger, on ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat hindlimb amputation model.J Surg Res. 2004 Aug;120(2):312-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2003.12.004. J Surg Res. 2004. PMID: 15234228
-
Can Cytoprotective Cobalt Protoporphyrin Protect Skeletal Muscle and Muscle-derived Stem Cells From Ischemic Injury?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Sep;473(9):2908-19. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4332-8. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 26070773 Free PMC article.
-
[Research and development of the free radical scavenger edaravone as a neuroprotectant].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2004 Mar;124(3):99-111. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.124.99. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15049127 Review. Japanese.
-
Neuroprotective effects of edaravone: a novel free radical scavenger in cerebrovascular injury.CNS Drug Rev. 2006 Spring;12(1):9-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2006.00009.x. CNS Drug Rev. 2006. PMID: 16834755 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective Role of Sulodexide on Renal Injury Induced by Limb Ischemia-Reperfusion.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jan 30;2021:6629718. doi: 10.1155/2021/6629718. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33564317 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid emulsion mitigates impaired pulmonary function induced by limb I/R in rats through attenuation of local cellular injury and the subsequent systemic inflammatory response/inflammation.BMC Anesthesiol. 2017 Jun 19;17(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12871-017-0375-6. BMC Anesthesiol. 2017. PMID: 28629353 Free PMC article.
-
Renoprotective effect of edaravone in acute limb ischemia/reperfusion injury.Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg. 2020 Apr 22;28(2):274-281. doi: 10.5606/tgkdc.dergisi.2020.18905. eCollection 2019 Jun. Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg. 2020. PMID: 32551157 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of vitamin E against acrylamide induced toxicity on skeletal muscles of adult male albino rat tongue: Light and electron microscopic study.J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2015 Jul-Sep;3(3):137-147. doi: 10.1016/j.jmau.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Mar 14. J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2015. PMID: 30023192 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of a half-course tourniquet strategy on peri-operative blood loss and early functional recovery in primary total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop. 2014 Feb;38(2):355-9. doi: 10.1007/s00264-013-2177-x. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Int Orthop. 2014. PMID: 24258152 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Crawford RS, Hashmi FF, Jones JE, Albadawi H, McCormack M, Eberlin K, Entabi F, Atkins MD, Conrad MF, Austen WG Jr. A novel model of acute murine hindlimb ischemia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292(2):H830–H837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

