Synapsin II gene expression in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of brain specimens from patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: effect of lifetime intake of antipsychotic drugs
- PMID: 23529008
- PMCID: PMC3970980
- DOI: 10.1038/tpj.2013.6
Synapsin II gene expression in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of brain specimens from patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: effect of lifetime intake of antipsychotic drugs
Abstract
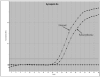
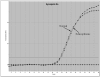
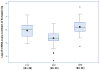
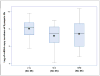
Synapsins are neuronal phosphoproteins crucial to regulating the processes required for normal neurotransmitter release. Synapsin II, in particular, has been implied as a candidate gene for schizophrenia. This study investigated synapsin II mRNA expression, using real-time reverse transcriptase-PCR, in coded dorsolateral prefrontal cortical samples provided by the Stanley Foundation Neuropathology Consortium. Synapsin IIa was decreased in patients with schizophrenia when compared with both healthy subjects and patients with bipolar disorder, whereas synapsin IIb was only significantly reduced in patients with schizophrenia when compared with healthy subjects but not in patients with bipolar disorder. Furthermore, lifetime antipsychotic drug use was positively associated with synapsin IIa expression in patients with schizophrenia. Results suggest that impairment of synaptic transmission by synapsin II reduction may contribute to dysregulated convergent molecular mechanisms, which result in aberrant neural circuits that characterize schizophrenia, while implicating involvement of synapsin II in therapeutic mechanisms of currently prescribed antipsychotic drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report neither competing financial interests nor potential conflicts of interest in relation to the work described.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Medial prefrontal cortical synapsin II knock-down induces behavioral abnormalities in the rat: examining synapsin II in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2011 Aug;130(1-3):250-9. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2011.05.017. Schizophr Res. 2011. PMID: 21689907
-
Atypical antipsychotic drugs upregulate synapsin II in the prefrontal cortex of post-mortem samples obtained from patients with schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2010 Jul;120(1-3):229-31. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2010.03.029. Schizophr Res. 2010. PMID: 20434888 No abstract available.
-
Antipsychotic drug use is correlated with CRP40/mortalin mRNA expression in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of human postmortem brain specimens.Schizophr Res. 2010 Jun;119(1-3):228-31. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2009.12.039. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Schizophr Res. 2010. PMID: 20100649
-
Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: findings from studies of the Stanley Foundation Brain Collection.Schizophr Res. 1999 Sep 29;39(2):149-52; discussion 163. doi: 10.1016/s0920-9964(99)00114-0. Schizophr Res. 1999. PMID: 10507526 Review.
-
Synapsin III: role in neuronal plasticity and disease.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Jun;22(4):416-24. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.07.007. Epub 2011 Jul 30. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21827867 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Expression of Synapsin I and II upon Treatment by Lithium and Valproic Acid in Various Brain Regions.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018 Jun 1;21(6):616-622. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyy023. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29618019 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Vesicle-Recycling Machinery Components as Potential Therapeutic Targets.Pharmacol Rev. 2017 Apr;69(2):141-160. doi: 10.1124/pr.116.013342. Pharmacol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28265000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Synapsins in Neurological Disorders.Neurosci Bull. 2018 Apr;34(2):349-358. doi: 10.1007/s12264-017-0201-7. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Neurosci Bull. 2018. PMID: 29282612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulations of Synaptic Vesicle Trafficking in Schizophrenia.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2016 Aug;18(8):77. doi: 10.1007/s11920-016-0710-5. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2016. PMID: 27371030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postmortem brain tissue as an underutilized resource to study the molecular pathology of neuropsychiatric disorders across different ethnic populations.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019 Jul;102:195-207. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.04.015. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019. PMID: 31028758 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dyck BA, Skoblenick KJ, Castellano JM, Ki K, Thomas N, Mishra RK. Behavioral abnormalities in synapsin II knockout mice implicate a causal factor in schizophrenia. Synapse. 2009;63(8):662–672. - PubMed
-
- Dyck BA, Mishra RK. Regulation of Synapsin II by Dopaminergic Mechanisms. Dopamine: Function, Regulation and Health Effects. New York: Nova Science Publishers; 2011.
-
- Dyck BA, Beyaert MG, Ferro MA, Mishra RK. Medial prefrontal cortical synapsin II knock-down induces behavioral abnormalities in the rat: Examining synapsin II in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2011;130(1–3):250–259. - PubMed
-
- Kasai K, Iwanami A, Yamasue H, Kuroki N, Nakagome K, Fukuda M. Neuroanatomy and neurophysiology in schizophrenia. Neurosci Res. 2002;43(2):93–110. - PubMed
-
- Goldman-Rakic PS. Working memory dysfunction in schizophrenia. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1994;6(4):348–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

