Cantharidin Impedes Activity of Glutathione S-Transferase in the Midgut of Helicoverpa armigera Hübner
- PMID: 23528854
- PMCID: PMC3634466
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms14035482
Cantharidin Impedes Activity of Glutathione S-Transferase in the Midgut of Helicoverpa armigera Hübner
Abstract
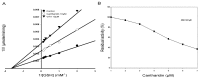
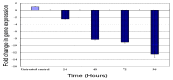
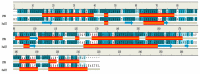
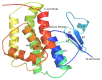
Previous investigations have implicated glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) as one of the major reasons for insecticide resistance. Therefore, effectiveness of new candidate compounds depends on their ability to inhibit GSTs to prevent metabolic detoxification by insects. Cantharidin, a terpenoid compound of insect origin, has been developed as a bio-pesticide in China, and proves highly toxic to a wide range of insects, especially lepidopteran. In the present study, we test cantharidin as a model compound for its toxicity, effects on the mRNA transcription of a model Helicoverpa armigera glutathione S-transferase gene (HaGST) and also for its putative inhibitory effect on the catalytic activity of GSTs, both in vivo and in vitro in Helicoverpa armigera, employing molecular and biochemical methods. Bioassay results showed that cantharidin was highly toxic to H. armigera. Real-time qPCR showed down-regulation of the HaGST at the mRNA transcript ranging from 2.5 to 12.5 folds while biochemical assays showed in vivo inhibition of GSTs in midgut and in vitro inhibition of rHaGST. Binding of cantharidin to HaGST was rationalized by homology and molecular docking simulations using a model GST (1PN9) as a template structure. Molecular docking simulations also confirmed accurate docking of the cantharidin molecule to the active site of HaGST impeding its catalytic activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of induced glutathione-S-transferase from Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) HaGST-8 in detoxification of pesticides.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018 Jan;147:612-621. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.028. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018. PMID: 28923727
-
Assessment of recombinant glutathione-S-transferase (HaGST-8) silica nano-conjugates for effective removal of pesticides.Environ Res. 2022 Mar;204(Pt B):112052. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112052. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 34597663
-
Molecular and biochemical characterization of the effects of insecticidal toxin from Meloidae beetles on Helicoverpa armigera (Hub.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).Genet Mol Res. 2013 Oct 10;12(4):4393-404. doi: 10.4238/2013.October.10.5. Genet Mol Res. 2013. PMID: 24222219
-
Overview of Cantharidin and its Analogues.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(17):2034-2044. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170414165253. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28413963 Review.
-
Mosquito glutathione transferases.Methods Enzymol. 2005;401:226-41. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)01014-1. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16399389 Review.
Cited by
-
Cap 'n' Collar C and Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Nuclear Translocator Facilitate the Expression of Glutathione S-Transferases Conferring Adaptation to Tannic Acid and Quercetin in Micromelalopha troglodyta (Graeser) (Lepidoptera: Notodontidae).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 22;24(3):2190. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032190. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768514 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Organ Involved in Cantharidin Biosynthesis in Epicauta chinensis Laporte (Coleoptera: Meloidae).J Insect Sci. 2017 Jan 1;17(2):52. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/iex021. J Insect Sci. 2017. PMID: 28423415 Free PMC article.
-
The Inhibition of Serine/Threonine Protein Phosphatase Type 5 Mediates Cantharidin Toxicity to Control Periplaneta americana (L.).Insects. 2020 Oct 8;11(10):682. doi: 10.3390/insects11100682. Insects. 2020. PMID: 33050059 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Changes in Chemosensory Gene Expression during the Dendrolimus punctatus Mating Process.Front Physiol. 2018 Jan 10;8:1127. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.01127. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29375398 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Juvenile Hormone Related Genes Regulating Cantharidin Biosynthesis in Epicauta chinensis.Sci Rep. 2017 May 23;7(1):2308. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02393-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28536442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayes J.D., Pulford D.J. The glutathione S-transferase supergene family-regulation of GST and the contribution of isozymes to cancer chemoprotection and drug resistance. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995;30:445–600. - PubMed
-
- Habig W.H., Pabst M.J., Jakoby W.B. Glutathione S-transferases. J. Biol. Chem. 1974;249:7130–7141. - PubMed
-
- Grant D.F., Dietze E.C., Hammock B.D. Glutathione S-transferase isozymes in Aedes aegypti: Purification, characterization and isozyme specific regulation. Insect Biochem. 1991;21:421–433.
-
- Huang H.S., Hu N.T., Yao Y.E., Wu C.Y., Chiang S.W., Sun C.N. Molecular cloning and heterologous expression of glutathione S-transferase involved in insecticide resistance from the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998;28:651–658. - PubMed
-
- Armes N.J., Jadhav D.R., Bond G.S., King A.B.S. Insecticide resistance in Helicoverpa armigera in South India. Pestic. Sci. 1992;34:355–364.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

