Shedding of discoidin domain receptor 1 by membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases
- PMID: 23519472
- PMCID: PMC3636896
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.409599
Shedding of discoidin domain receptor 1 by membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases
Abstract
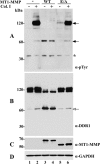
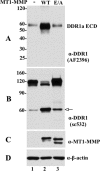
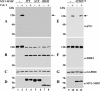
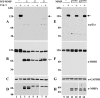
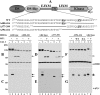
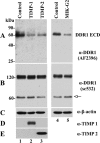
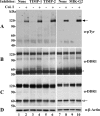
The discoidin domain receptors (DDRs) are receptor tyrosine kinases that upon binding to collagens undergo receptor phosphorylation, which in turn activates signal transduction pathways that regulate cell-collagen interactions. We report here that collagen-dependent DDR1 activation is partly regulated by the proteolytic activity of the membrane-anchored collagenases, MT1-, MT2-, and MT3-matrix metalloproteinase (MMP). These collagenases cleave DDR1 and attenuate collagen I- and IV-induced receptor phosphorylation. This effect is not due to ligand degradation, as it proceeds even when the receptor is stimulated with collagenase-resistant collagen I (r/r) or with a triple-helical peptide harboring the DDR recognition motif in collagens. Moreover, the secreted collagenases MMP-1 and MMP-13 and the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane-type MMPs (MT4- and MT6-MMP) have no effect on DDR1 cleavage or activation. N-terminal sequencing of the MT1-MMP-mediated cleaved products and mutational analyses show that cleavage of DDR1 takes place within the extracellular juxtamembrane region, generating a membrane-anchored C-terminal fragment. Metalloproteinase inhibitor studies show that constitutive shedding of endogenous DDR1 in breast cancer HCC1806 cells is partly mediated by MT1-MMP, which also regulates collagen-induced receptor activation. Taken together, these data suggest a role for the collagenase of membrane-type MMPs in regulation of DDR1 cleavage and activation at the cell-matrix interface.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Collagen type I selectively activates ectodomain shedding of the discoidin domain receptor 1: involvement of Src tyrosine kinase.J Cell Biochem. 2006 Jun 1;98(3):672-84. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20812. J Cell Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16440311 Free PMC article.
-
Role of DDR1 in the gelatinases secretion induced by native type IV collagen in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2011 Jun;28(5):463-77. doi: 10.1007/s10585-011-9385-9. Epub 2011 Apr 2. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2011. PMID: 21461859
-
Collagen binding specificity of the discoidin domain receptors: binding sites on collagens II and III and molecular determinants for collagen IV recognition by DDR1.Matrix Biol. 2011 Jan;30(1):16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2010.10.004. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Matrix Biol. 2011. PMID: 21044884 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen recognition and transmembrane signalling by discoidin domain receptors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1834(10):2187-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.10.014. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23128141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discoidin domain receptors in disease.Matrix Biol. 2014 Feb;34:185-92. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Matrix Biol. 2014. PMID: 24361528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular matrix remodeling in tumor progression and immune escape: from mechanisms to treatments.Mol Cancer. 2023 Mar 11;22(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01744-8. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36906534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Microenvironment Signals by Proteolytic Shedding of Cell Surface Extracellular Matrix Receptors.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 2;9:736735. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.736735. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34796172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eph- and ephrin-dependent mechanisms in tumor and stem cell dynamics.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Oct;71(19):3685-710. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1633-0. Epub 2014 May 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24794629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discoidin domain receptors orchestrate cancer progression: A focus on cancer therapies.Cancer Sci. 2021 Mar;112(3):962-969. doi: 10.1111/cas.14789. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33377205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ADAM10 controls collagen signaling and cell migration on collagen by shedding the ectodomain of discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1).Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Feb 15;26(4):659-73. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-10-1463. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25540428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leitinger B. (2011) Transmembrane collagen receptors. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 27, 265–290 - PubMed
-
- Vogel W. F., Abdulhussein R., Ford C. E. (2006) Sensing extracellular matrix: an update on discoidin domain receptor function. Cell. Signal. 18, 1108–1116 - PubMed
-
- Vogel W., Gish G. D., Alves F., Pawson T. (1997) The discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinases are activated by collagen. Mol. Cell 1, 13–23 - PubMed
-
- Shrivastava A., Radziejewski C., Campbell E., Kovac L., McGlynn M., Ryan T. E., Davis S., Goldfarb M. P., Glass D. J., Lemke G., Yancopoulos G. D. (1997) An orphan receptor tyrosine kinase family whose members serve as nonintegrin collagen receptors. Mol. Cell 1, 25–34 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

