Intervention of electroacupuncture on spinal p38 MAPK/ATF-2/VR-1 pathway in treating inflammatory pain induced by CFA in rats
- PMID: 23517865
- PMCID: PMC3608238
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-9-13
Intervention of electroacupuncture on spinal p38 MAPK/ATF-2/VR-1 pathway in treating inflammatory pain induced by CFA in rats
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have demonstrated that p38 MAPK signal transduction pathway plays an important role in the development and maintenance of inflammatory pain. Electroacupuncture (EA) can suppress the inflammatory pain. However, the relationship between EA effect and p38 MAPK signal transduction pathway in inflammatory pain remains poorly understood. It is our hypothesis that p38 MAPK/ATF-2/VR-1 and/or p38 MAPK/ATF-2/COX-2 signal transduction pathway should be activated by inflammatory pain in CFA-injected model. Meanwhile, EA may inhibit the activation of p38 MAPK signal transduction pathway. The present study aims to investigate that anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect of EA and its intervention on the p38 MAPK signal transduction pathway in a rat model of inflammatory pain.
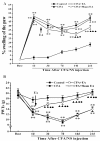
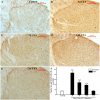
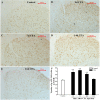
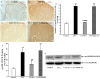
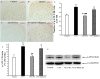
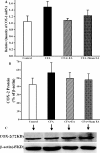
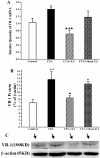
Results: EA had a pronounced anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect on CFA-induced chronic inflammatory pain in rats. EA could quickly raise CFA-rat's paw withdrawal thresholds (PWTs) and maintain good and long analgesic effect, while it subdued the ankle swelling of CFA rats only at postinjection day 14. EA could down-regulate the protein expressions of p-p38 MAPK and p-ATF-2, reduced the numbers of p-p38 MAPK-IR cells and p-ATF-2-IR cells in spinal dorsal horn in CFA rats, inhibited the expressions of both protein and mRNA of VR-1, but had no effect on the COX-2 mRNA expression.
Conclusions: The present study indicates that inhibiting the activation of spinal p38 MAPK/ATF-2/VR-1 pathway may be one of the main mechanisms via central signal transduction pathway in the process of anti-inflammatory pain by EA in CFA rats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture attenuates mechanical allodynia by suppressing the spinal JNK1/2 pathway in a rat model of inflammatory pain.Brain Res Bull. 2014 Sep;108:27-36. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2014.06.004. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Brain Res Bull. 2014. PMID: 25010483
-
Electroacupuncture attenuates spinal nerve ligation-induced microglial activation mediated by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.Chin J Integr Med. 2016 Sep;22(9):704-13. doi: 10.1007/s11655-015-2045-1. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Chin J Integr Med. 2016. PMID: 25847774
-
[Immediate analgesic effect of electroacupuncture and its regulation mechanism via spinal p-ERK1/2].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2012 Nov;32(11):1007-11. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2012. PMID: 23213989 Chinese.
-
Effect of Acupuncture on the p38 Signaling Pathway in Several Nervous System Diseases: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 30;21(13):4693. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134693. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32630156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function and inhibition of P38 MAP kinase signaling: Targeting multiple inflammation diseases.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 Feb;220:115973. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115973. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38103797 Review.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture Alleviates Pain Responses and Inflammation in a Rat Model of Acute Gout Arthritis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Mar 19;2018:2598975. doi: 10.1155/2018/2598975. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 29743920 Free PMC article.
-
Strong Manual Acupuncture Stimulation of "Huantiao" (GB 30) Reduces Pain-Induced Anxiety and p-ERK in the Anterior Cingulate Cortex in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:235491. doi: 10.1155/2015/235491. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26770252 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the cAMP/PKA/CREB Pathway Contributes to the Analgesic Effects of Electroacupuncture in the Anterior Cingulate Cortex in a Rat Pain Memory Model.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:5320641. doi: 10.1155/2016/5320641. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 28090359 Free PMC article.
-
Alleviating Mechanical Allodynia and Modulating Cellular Immunity Contribute to Electroacupuncture's Dual Effect on Bone Cancer Pain.Integr Cancer Ther. 2018 Jun;17(2):401-410. doi: 10.1177/1534735417728335. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Integr Cancer Ther. 2018. PMID: 28870114 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Electroacupuncture with Dominant Frequency at SP 6 and ST 36 Based on Meridian Theory on Pain-Depression Dyad in Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:732845. doi: 10.1155/2015/732845. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 25821498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bombardier C, Laine L, Reicin A, Shapiro D, Burgos-Vargas R, Davis B, Day R, Ferraz MB, Hawkey CJ, Hochberg MC, Kvien TK, Schnitzer TJ. VIGOR StudyGroup. Comparison of upper gastrointestinal toxicity of rofecoxib and naproxen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. VIGOR Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1520–1528. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200011233432103. 1522 p following 1528. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

