Computational small RNA prediction in bacteria
- PMID: 23516022
- PMCID: PMC3596055
- DOI: 10.4137/BBI.S11213
Computational small RNA prediction in bacteria
Abstract
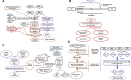
Bacterial, small RNAs were once regarded as potent regulators of gene expression and are now being considered as essential for their diversified roles. Many small RNAs are now reported to have a wide array of regulatory functions, ranging from environmental sensing to pathogenesis. Traditionally, noncoding transcripts were rarely detected by means of genetic screens. However, the availability of approximately 2200 prokaryotic genome sequences in public databases facilitates the efficient computational search of those molecules, followed by experimental validation. In principle, the following four major computational methods were applied for the prediction of sRNA locations from bacterial genome sequences: (1) comparative genomics, (2) secondary structure and thermodynamic stability, (3) 'Orphan' transcriptional signals and (4) ab initio methods regardless of sequence or structure similarity; most of these tools were applied to locate the putative genomic sRNA locations followed by experimental validation of those transcripts. Therefore, computational screening has simplified the sRNA identification process in bacteria. In this review, a plethora of small RNA prediction methods and tools that have been reported in the past decade are discussed comprehensively and assessed based on their attributes, compatibility, and their prediction accuracy.
Keywords: base composition; comparative genomics; ncRNA; sRNA prediction; structure stability; transcriptional signal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An Experimental Approach to Genome Annotation: This report is based on a colloquium sponsored by the American Academy of Microbiology held July 19-20, 2004, in Washington, DC.Washington (DC): American Society for Microbiology; 2004. Washington (DC): American Society for Microbiology; 2004. PMID: 33001599 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
sRNA Target Prediction Organizing Tool (SPOT) Integrates Computational and Experimental Data To Facilitate Functional Characterization of Bacterial Small RNAs.mSphere. 2019 Jan 30;4(1):e00561-18. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00561-18. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 30700509 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Prediction of sRNA in Acinetobacter baumannii.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1946:307-320. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9118-1_27. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30798565
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of small RNAs in Rhodobacter capsulatus and identification of small RNAs affected by loss of the response regulator CtrA.RNA Biol. 2017 Jul 3;14(7):914-925. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1306175. Epub 2017 Mar 15. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 28296577 Free PMC article.
-
A Hitchhiker's guide to RNA-RNA structure and interaction prediction tools.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Nov 22;25(1):bbad421. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad421. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 38040490 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PresRAT: a server for identification of bacterial small-RNA sequences and their targets with probable binding region.RNA Biol. 2021 Aug;18(8):1152-1159. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1836455. Epub 2020 Oct 25. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33103602 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Fecal Small RNA Profiles in Colorectal Cancer Reflect Gut Microbiome Composition in Stool Samples.mSystems. 2019 Sep 17;4(5):e00289-19. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00289-19. mSystems. 2019. PMID: 31530647 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of ethanol-responsive small RNAs in Zymomonas mobilis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Jul;80(14):4189-98. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00429-14. Epub 2014 May 2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24795378 Free PMC article.
-
A Genome-Wide Prediction and Identification of Intergenic Small RNAs by Comparative Analysis in Mesorhizobium huakuii 7653R.Front Microbiol. 2017 Sep 8;8:1730. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01730. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28943874 Free PMC article.
-
An improved method for identification of small non-coding RNAs in bacteria using support vector machine.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 6;7:46070. doi: 10.1038/srep46070. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28383059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huttenhofer A, Schattner P, Polacek N. Noncoding RNAs: hope or hype? Trends Genet. 2005;21:289–97. - PubMed
-
- Johansson J, Cossart P. RNA-mediated control of virulence gene expression in bacterial pathogens. Trends Microbiol. 2003;11:280–5. - PubMed
-
- Nelson P, Kiriakidou M, Sharma A, Maniataki E, Mourelatos Z. The microRNA world: small is mighty. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28:534–40. - PubMed
-
- Papenfort K, Vogel J. Regulatory RNA in Bacterial Pathogens. Cell Host and Microbe. 2010;8:116–27. - PubMed
-
- Postic G, Frapy E, Dupuis M, et al. Regulation of virulence in Francisella tularensis by small noncoding RNAs. Nature Preceedings. 2011 doi: 10.1038/npre.2011.5965.1. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

