The tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 regulates focal adhesion kinase to promote EGF-induced lamellipodia persistence and cell migration
- PMID: 23512980
- PMCID: PMC3686999
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0578
The tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 regulates focal adhesion kinase to promote EGF-induced lamellipodia persistence and cell migration
Abstract
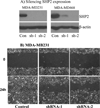
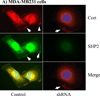
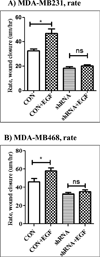
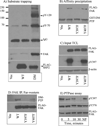
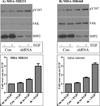
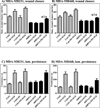
The Src homology phosphotyrosyl phosphatase 2 (SHP2) is a positive effector of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) signaling. Furthermore, SHP2 is known to promote cell migration and invasiveness, key steps in cancer metastasis. To date, however, the mechanism by which SHP2 regulates cell movement is not fully understood. In the current report, a new role for SHP2 in regulating cell migration has been suggested. We show that SHP2 mediates lamellipodia persistence and cell polarity to promote directional cell migration in the MDA-MB231 and the MDA-MB468 basal-like and triple-negative breast cancer cell lines. We further show that SHP2 modulates the activity of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) by dephosphorylating pTyr397, the autophosphorylation site that primes FAK function. Because hyperactivation of FAK is known to counter the maturation of nascent focal complexes to focal adhesions, we propose that one of the mechanisms by which SHP2 promotes lamellipodia persistence is by downregulating FAK activity through dephosphorylation of pTyr397. The finding that inhibition of FAK activity partially restores EGF-induced lamellipodia persistence and cell migration in SHP2-silenced cells supports our proposition that SHP2 promotes growth factor-induced cell movement by acting, at least in part, on FAK. However, the effect of SHP2 inhibition in nonstimulated cells seems FAK independent as there was no significant difference between the control and the SHP2-silenced cells in pY397-FAK levels. Also, FAK inhibition did not rescue Golgi orientation defects in SHP2-silenced cells, suggesting that SHP2 acts through other mechanisms to promote cell polarity.
©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures








Similar articles
-
Deoxycholic acid differentially regulates focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation: role of tyrosine phosphatase ShP2.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006 Dec;291(6):G1100-12. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00008.2006. Epub 2006 Aug 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16920701
-
Shp2 negatively regulates growth in cardiomyocytes by controlling focal adhesion kinase/Src and mTOR pathways.Circ Res. 2008 Oct 10;103(8):813-24. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.179754. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18757826
-
CB₁ cannabinoid receptors promote maximal FAK catalytic activity by stimulating cooperative signaling between receptor tyrosine kinases and integrins in neuronal cells.Cell Signal. 2013 Aug;25(8):1665-77. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.03.020. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23571270 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into FAK structure and function in focal adhesions.J Cell Sci. 2022 Oct 15;135(20):jcs259089. doi: 10.1242/jcs.259089. Epub 2022 Oct 14. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 36239192 Review.
-
The role of FAK in tumor metabolism and therapy.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 May;142(2):154-63. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.12.003. Epub 2013 Dec 9. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24333503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ZINC40099027 activates human focal adhesion kinase by accelerating the enzymatic activity of the FAK kinase domain.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2021 Apr;9(2):e00737. doi: 10.1002/prp2.737. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2021. PMID: 33715263 Free PMC article.
-
The tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 associates with CUB domain-containing protein-1 (CDCP1), regulating its expression at the cell surface in a phosphorylation-dependent manner.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 13;10(4):e0123472. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123472. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25876044 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting protein tyrosine phosphatase signaling by engineered chemogenetic control of its activity.J Cell Biol. 2022 Aug 1;221(8):e202111066. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202111066. Epub 2022 Jul 13. J Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35829702 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0084443 Is Upregulated in Diabetic Foot Ulcer and Modulates Keratinocyte Migration and Proliferation.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2020 Apr 1;9(4):145-160. doi: 10.1089/wound.2019.0956. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2020. PMID: 32117579 Free PMC article.
-
A specific amino acid context in EGFR and HER2 phosphorylation sites enables selective binding to the active site of Src homology phosphatase 2 (SHP2).J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 13;295(11):3563-3575. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011422. Epub 2020 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32024694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sugimoto S, Lechleider RJ, Shoelson SE, Neel BG, Walsh CT. Expression, purification, and characterization of SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase, SH-PTP2. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1993;268(30) 22771-. - PubMed
-
- Hof P, Pluskey S, Dhe-Paganon S, Eck MJ, Shoelson SE. Crystal structure of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2. Cell. 1998 Feb 20;92(4):441–450. - PubMed
-
- Qu CK. The SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase: signaling mechanisms and biological functions. Cell Research. 2000;10(4):279–288. - PubMed
-
- Higashi H, Nakaya A, Tsutsumi R, Yokoyama K, Fujii Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Helicobacter pylori CagA induces Ras-independent morphogenetic response through SHP-2 recruitment and activation. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2004;279(17):17205–17216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

