Postsynaptic density scaffold SAP102 regulates cortical synapse development through EphB and PAK signaling pathway
- PMID: 23486974
- PMCID: PMC3632365
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2896-12.2013
Postsynaptic density scaffold SAP102 regulates cortical synapse development through EphB and PAK signaling pathway
Abstract
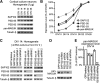
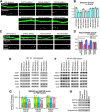
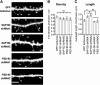
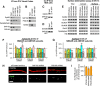
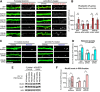
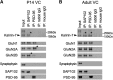
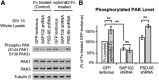
Membrane-associated guanylate kinases (MAGUKs), including SAP102, PSD-95, PSD-93, and SAP97, are scaffolding proteins for ionotropic glutamate receptors at excitatory synapses. MAGUKs play critical roles in synaptic plasticity; however, details of signaling roles for each MAGUK remain largely unknown. Here we report that SAP102 regulates cortical synapse development through the EphB and PAK signaling pathways. Using lentivirus-delivered shRNAs, we found that SAP102 and PSD-95, but not PSD-93, are necessary for excitatory synapse formation and synaptic AMPA receptor (AMPAR) localization in developing mouse cortical neurons. SAP102 knockdown (KD) increased numbers of elongated dendritic filopodia, which is often observed in mouse models and human patients with mental retardation. Further analysis revealed that SAP102 coimmunoprecipitated the receptor tyrosine kinase EphB2 and RacGEF Kalirin-7 in neonatal cortex, and SAP102 KD reduced surface expression and dendritic localization of EphB. Moreover, SAP102 KD prevented reorganization of actin filaments, synapse formation, and synaptic AMPAR trafficking in response to EphB activation triggered by its ligand ephrinB. Last, p21-activated kinases (PAKs) were downregulated in SAP102 KD neurons. These results demonstrate that SAP102 has unique roles in cortical synapse development by mediating EphB and its downstream PAK signaling pathway. Both SAP102 and PAKs are associated with X-linked mental retardation in humans; thus, synapse formation mediated by EphB/SAP102/PAK signaling in the early postnatal brain may be crucial for cognitive development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NMDA receptor-dependent regulation of dendritic spine morphology by SAP102 splice variants.J Neurosci. 2011 Jan 5;31(1):89-96. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1034-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21209193 Free PMC article.
-
SAP102 regulates synaptic AMPAR function through a CNIH-2-dependent mechanism.J Neurophysiol. 2018 Oct 1;120(4):1578-1586. doi: 10.1152/jn.00731.2017. Epub 2018 Aug 1. J Neurophysiol. 2018. PMID: 30067114 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of A-kinase anchoring protein 79/150-cAMP-dependent protein kinase postsynaptic targeting by NMDA receptor activation of calcineurin and remodeling of dendritic actin.J Neurosci. 2002 Aug 15;22(16):7027-44. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-16-07027.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12177200 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
-
MAGUKs, synaptic development, and synaptic plasticity.Neuroscientist. 2011 Oct;17(5):493-512. doi: 10.1177/1073858410386384. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Neuroscientist. 2011. PMID: 21498811 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Subunit-specific regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor trafficking by SAP102 protein splice variants.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 20;290(8):5105-5116. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.599969. Epub 2015 Jan 2. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25555912 Free PMC article.
-
Role of actin cytoskeleton in the organization and function of ionotropic glutamate receptors.Curr Res Struct Biol. 2021 Oct 14;3:277-289. doi: 10.1016/j.crstbi.2021.10.001. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Struct Biol. 2021. PMID: 34766008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of nascent and active zone ultrastructure as synapses enlarge during long-term potentiation in mature hippocampus.J Comp Neurol. 2014 Dec 1;522(17):3861-84. doi: 10.1002/cne.23646. Epub 2014 Jul 30. J Comp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25043676 Free PMC article.
-
Trafficking of kainate receptors.Membranes (Basel). 2014 Aug 20;4(3):565-95. doi: 10.3390/membranes4030565. Membranes (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25141211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid homeostatic downregulation of LTP by extrasynaptic GluN2B receptors.J Neurophysiol. 2018 Nov 1;120(5):2351-2357. doi: 10.1152/jn.00421.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 15. J Neurophysiol. 2018. PMID: 30110236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen KM, Gleeson JG, Bagrodia S, Partington MW, MacMillan JC, Cerione RA, Mulley JC, Walsh CA. PAK3 mutation in nonsyndromic X-linked mental retardation. Nat Genet. 1998;20:25–30. - PubMed
-
- Banker G, Goslin K. Culturing nerve cells. Cambridge, MA: MIT; 1991.
-
- Bienvenu T, des Portes V, McDonell N, Carrié A, Zemni R, Couvert P, Ropers HH, Moraine C, van Bokhoven H, Fryns JP, Allen K, Walsh CA, Boué J, Kahn A, Chelly J, Beldjord C. Missense mutation in PAK3, R67C, causes X-linked nonspecific mental retardation. Am J Med Genet. 2000;93:294–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
