Mutations in phospholipase DDHD2 cause autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia (SPG54)
- PMID: 23486545
- PMCID: PMC3798837
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2013.29
Mutations in phospholipase DDHD2 cause autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia (SPG54)
Abstract
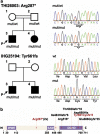
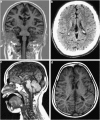
Hereditary spastic paraplegias (HSP) are a genetically heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by a distal axonopathy of the corticospinal tract motor neurons leading to progressive lower limb spasticity and weakness. Intracellular membrane trafficking, mitochondrial dysfunction and myelin formation are key functions involved in HSP pathogenesis. Only recently defects in metabolism of complex lipids have been implicated in a number of HSP subtypes. Mutations in the 23 known autosomal recessive HSP genes explain less than half of autosomal recessive HSP cases. To identify novel autosomal recessive HSP disease genes, exome sequencing was performed in 79 index cases with autosomal recessive forms of HSP. Resulting variants were filtered and intersected between families to allow identification of new disease genes. We identified two deleterious mutations in the phospholipase DDHD2 gene in two families with complicated HSP. The phenotype is characterized by early onset of spastic paraplegia, mental retardation, short stature and dysgenesis of the corpus callosum. Phospholipase DDHD2 is involved in intracellular membrane trafficking at the golgi/ endoplasmic reticulum interface and has been shown to possess phospholipase A1 activity in vitro. Discovery of DDHD2 mutations in HSP might therefore provide a link between two key pathogenic themes in HSP: membrane trafficking and lipid metabolism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutations in CYP2U1, DDHD2 and GBA2 genes are rare causes of complicated forms of hereditary spastic paraparesis.J Neurol. 2014 Feb;261(2):373-81. doi: 10.1007/s00415-013-7206-6. Epub 2013 Dec 13. J Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24337409
-
Mutations in DDHD2, encoding an intracellular phospholipase A(1), cause a recessive form of complex hereditary spastic paraplegia.Am J Hum Genet. 2012 Dec 7;91(6):1073-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.10.017. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Am J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 23176823 Free PMC article.
-
Truncating mutation in intracellular phospholipase A₁ gene (DDHD2) in hereditary spastic paraplegia with intellectual disability (SPG54).BMC Res Notes. 2015 Jun 27;8:271. doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1227-4. BMC Res Notes. 2015. PMID: 26113134 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of hereditary spastic paraplegias.Semin Neurol. 2011 Nov;31(5):484-93. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1299787. Epub 2012 Jan 21. Semin Neurol. 2011. PMID: 22266886 Review.
-
Clinical features and management of hereditary spastic paraplegia.Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2014 Mar;72(3):219-26. doi: 10.1590/0004-282x20130248. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2014. PMID: 24676440 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein purification and cloning of diacylglycerol lipase from rat brain.J Biochem. 2016 Jun;159(6):585-97. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvw002. Epub 2016 Jan 19. J Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26790472 Free PMC article.
-
NT5C2 novel splicing variant expands the phenotypic spectrum of Spastic Paraplegia (SPG45): case report of a new member of thin corpus callosum SPG-Subgroup.BMC Med Genet. 2017 Mar 21;18(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12881-017-0395-6. BMC Med Genet. 2017. PMID: 28327087 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of lipids for upper motor neuron health and disease.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr;112:92-104. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.11.004. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33323321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional roles of ADP-ribosylation writers, readers and erasers.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 11;10:941356. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.941356. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36035988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphatidic acid phospholipase A1 mediates ER-Golgi transit of a family of G protein-coupled receptors.J Cell Biol. 2014 Jul 7;206(1):79-95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201405020. J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25002678 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

