Protection from articular damage by passive or active anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α immunotherapy in human TNF-α transgenic mice depends on anti-TNF-α antibody levels
- PMID: 23480185
- PMCID: PMC3719931
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12040
Protection from articular damage by passive or active anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α immunotherapy in human TNF-α transgenic mice depends on anti-TNF-α antibody levels
Abstract
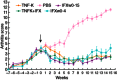
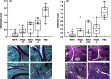
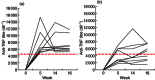
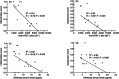
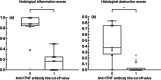
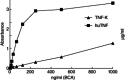
Active anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α immunization with the kinoid of TNF-α (TNF-K) induces polyclonal anti-TNF-α antibodies and ameliorates arthritis in human TNF-α (hTNF-α) transgenic mice (TTg). We compared the efficacy of TNF-K to that of infliximab (IFX) and of TNF-K and IFX co-administration, and evaluated whether the titres of anti-hTNF-α antibodies induced by immunization were a determinant of TNF-K efficacy. Forty-eight TTg mice received one of the following treatments: TNF-K immunization (TNF-K group); weekly IFX throughout the study duration (IFXw0-15); TNF-K plus weekly IFX for 4 weeks (TNF-K + IFX); and weekly IFX for 4 weeks (IFXw0-4); PBS. Animals were killed at week 16. Anti-hTNF-α antibody titres and clinical and histological scores were compared. All TNF-K immunized mice (TNF-K and TNF-K + IFX) produced anti-hTNF-α antibodies. Titres were higher in TNF-K versus TNF-K + IFX (P < 0·001) and correlated inversely with histological inflammation (R = -0·78; P = 0·0001) and destruction (R = -0·67; P = 0·001). TNF-K + IFX had higher histological inflammation and destruction versus TNF-K (P < 0·05). A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis of anti-hTNF-α antibody titres identified the criterion cut-off value to discriminate most effectively between the TNF-K and TNF-K + IFX groups. Mice with high versus low titres had less histological inflammation and destruction (P < 0·05). In a model of TNF-α-dependent arthritis, protection from articular damage by TNF-K correlates with the titres of induced anti-hTNF-α antibodies. The co-administration of TNF-K and a short course of infliximab does not result in less articular damage versus solely TNF-K, due probably to lower anti-hTNF-α antibody production. These results are relevant for future development of active anti-TNF-α immunization in human disease.
© 2012 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Active immunization to tumor necrosis factor-alpha is effective in treating chronic established inflammatory disease: a long-term study in a transgenic model of arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(6):R195. doi: 10.1186/ar2897. Epub 2009 Dec 23. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 20030816 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of anti-nuclear antibodies is a risk factor for the appearance of anti-drug antibodies during infliximab or adalimumab therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 14;15(12):e0243729. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243729. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33315881 Free PMC article.
-
[Association of short-term efficacy for infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis with plasma concentration and anti-drug antibody].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 Sep 28;43(9):982-986. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2018.09.008. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018. PMID: 30333289 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Anti-TNF alpha therapy of rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned?Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:163-96. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.163. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11244034 Review.
-
[Anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibodies in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis].Rev Med Interne. 2000 Oct;21(10):854-62. doi: 10.1016/s0248-8663(00)00236-8. Rev Med Interne. 2000. PMID: 11075394 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic vaccination with TNF-Kinoid in TNF antagonist-resistant rheumatoid arthritis: a phase II randomized, controlled clinical trial.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 17;9(12):e113465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113465. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25517733 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Development of a Recombinant Xenogeneic Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Protein Vaccine To Protect Mice from Experimental Colitis.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015 Dec;22(12):1269-75. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00331-15. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26466602 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Targeting Can Protect against Arthritis with Low Sensitization to Infection.Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 14;8:1533. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01533. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29184553 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1 Vaccination Is Suitable for Treating Inflammatory Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jan 31;8:6. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00006. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28197099 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Localization of Therapeutic Fab-CHP Conjugates to Sites of Denatured Collagen for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Bioconjug Chem. 2020 Aug 19;31(8):1960-1970. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.0c00324. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Bioconjug Chem. 2020. PMID: 32609496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sfikakis PP. The first decade of biologic TNF antagonists in clinical practice: lessons learned, unresolved issues and future directions. Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2010;11:180–210. - PubMed
-
- Gaujoux-Viala C, Mouterde G, Baillet A, et al. Evaluating disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: which composite index is best? A systematic literature analysis of studies comparing the psychometric properties of the DAS, DAS28, SDAI and CDAI. Joint Bone Spine. 2012;79:149–155. - PubMed
-
- Hetland ML, Christensen IJ, Tarp U, et al. Direct comparison of treatment responses, remission rates, and drug adherence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with adalimumab, etanercept, or infliximab: results from eight years of surveillance of clinical practice in the nationwide Danish DANBIO registry. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:22–32. - PubMed
-
- Russell AS. Quality-of-life assessment in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics. 2008;26:831–846. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

