Efficient and specific gene knockdown by small interfering RNAs produced in bacteria
- PMID: 23475073
- PMCID: PMC3622153
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.2537
Efficient and specific gene knockdown by small interfering RNAs produced in bacteria
Abstract
Synthetic small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are an indispensable tool to investigate gene function in eukaryotic cells and may be used for therapeutic purposes to knock down genes implicated in disease. Thus far, most synthetic siRNAs have been produced by chemical synthesis. Here we present a method to produce highly potent siRNAs in Escherichia coli. This method relies on ectopic expression of p19, an siRNA-binding protein found in a plant RNA virus. When expressed in E. coli, p19 stabilizes an ∼21-nt siRNA-like species produced by bacterial RNase III. When mammalian cells are transfected by them, siRNAs that were generated in bacteria expressing p19 and a hairpin RNA encoding 200 or more nucleotides of a target gene reproducibly knock down target gene expression by ∼90% without immunogenicity or off-target effects. Because bacterially produced siRNAs contain multiple sequences against a target gene, they may be especially useful for suppressing polymorphic cellular or viral genes.
Figures
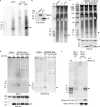

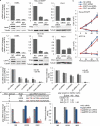
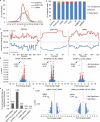
Comment in
-
Renewable RNAi.Nat Biotechnol. 2013 Apr;31(4):319-20. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2547. Nat Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23563428 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Production of highly potent recombinant siRNAs in Escherichia coli.Nat Protoc. 2013 Dec;8(12):2325-36. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.149. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Nat Protoc. 2013. PMID: 24177290
-
Milligram scale production of potent recombinant small interfering RNAs in Escherichia coli.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2018 Sep;115(9):2280-2291. doi: 10.1002/bit.26740. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2018. PMID: 29873060
-
Tombusvirus p19 Captures RNase III-Cleaved Double-Stranded RNAs Formed by Overlapping Sense and Antisense Transcripts in Escherichia coli.mBio. 2020 Jun 9;11(3):e00485-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00485-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32518184 Free PMC article.
-
[New progress of the highly efficient siRNA design].Yi Chuan. 2006 Nov;28(11):1457-61. doi: 10.1360/yc-006-1457. Yi Chuan. 2006. PMID: 17098718 Review. Chinese.
-
Targeted gene silencing by small interfering RNA-based knock-down technology.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2004 Feb;5(1):1-7. doi: 10.2174/1389201043489558. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 14965205 Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of RNA interference targeting Bactrocera dorsalis ds-Bdrpl19 on the gene expression of rpl19 in non-target insects.Ecotoxicology. 2015 Apr;24(3):595-603. doi: 10.1007/s10646-014-1407-3. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Ecotoxicology. 2015. PMID: 25567188
-
Myeloid Cells in Intact Human Cervical Explants Capture HIV and Can Transmit It to CD4 T Cells.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 23;9:2719. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02719. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30532754 Free PMC article.
-
The Combination of Bacillus Thuringiensis and Its Engineered Strain Expressing dsRNA Increases the Toxicity against Plutella Xylostella.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 31;23(1):444. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010444. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008871 Free PMC article.
-
Production of highly potent recombinant siRNAs in Escherichia coli.Nat Protoc. 2013 Dec;8(12):2325-36. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.149. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Nat Protoc. 2013. PMID: 24177290
-
Bioengineered Noncoding RNAs Selectively Change Cellular miRNome Profiles for Cancer Therapy.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018 Jun;365(3):494-506. doi: 10.1124/jpet.118.247775. Epub 2018 Mar 30. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018. PMID: 29602831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elbashir SM, et al. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001;411:494–498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

