Conformational epitope consisting of the V3 and V4 loops as a target for potent and broad neutralization of simian immunodeficiency viruses
- PMID: 23468483
- PMCID: PMC3648159
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00201-13
Conformational epitope consisting of the V3 and V4 loops as a target for potent and broad neutralization of simian immunodeficiency viruses
Abstract
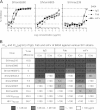
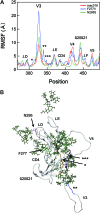
Inducing neutralizing antibodies (NAb) is the key to developing a protective vaccine against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). To clarify the neutralization mechanism of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), we analyzed NAb B404, which showed potent and broad neutralizing activity against various SIV strains. In 4 SIVsmH635FC-infected macaques, B404-like antibodies using the specific VH3 gene with a long complementarity-determining region 3 loop and λ light chain were the major NAbs in terms of the number and neutralizing potency. This biased NAb induction was observed in all 4 SIVsmH635FC-infected macaques but not in 2 macaques infected with a SIV mix, suggesting that induction of B404-like NAbs depended on the inoculated virus. Analysis using Env mutants revealed that the V3 and V4 loops were critical for B404 binding. The reactivity to the B404 epitope on trimeric, but not monomeric, Env was enhanced by CD4 ligation. The B404-resistant variant, which was induced by passages with increasing concentrations of B404, accumulated amino acid substitutions in the C2 region of gp120. Molecular dynamics simulations of the gp120 outer domains indicated that the C2 mutations could effectively alter the structural dynamics of the V3/V4 loops and their neighboring regions. These results suggest that a conformational epitope consisting of the V3 and V4 loops is the target for potent and broad neutralization of SIV. Identifying the new neutralizing epitope, as well as specifying the VH3 gene used for epitope recognition, will help to develop HIV-1 vaccines.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Envelope variable region 4 is the first target of neutralizing antibodies in early simian immunodeficiency virus mac251 infection of rhesus monkeys.J Virol. 2012 Jul;86(13):7052-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00107-12. Epub 2012 Apr 24. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22532675 Free PMC article.
-
Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) envelope-specific Fabs with high-level homologous neutralizing activity: recovery from a long-term-nonprogressor SIV-infected macaque.J Virol. 1998 Jan;72(1):585-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.1.585-592.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9420262 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies and Their Mapping by Monomeric gp120 in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1-Infected Humans and Simian-Human Immunodeficiency Virus SHIVSF162P3N-Infected Macaques.J Virol. 2016 Mar 28;90(8):4017-4031. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02898-15. Print 2016 Apr. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26842476 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-neutralization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and 2 and simian immunodeficiency virus isolates.J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3602-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.66.6.3602-3608.1992. J Virol. 1992. PMID: 1374810 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of Fas ligand by simian immunodeficiency virus - a nef-arious mechanism of immune evasion?J Exp Med. 1997 Jul 7;186(1):1-5. doi: 10.1084/jem.186.1.1. J Exp Med. 1997. PMID: 9207006 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Human Antibodies that Recognize Novel Immunodominant Quaternary Epitopes on the HIV-1 Env Protein.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 13;11(7):e0158861. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158861. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27411063 Free PMC article.
-
A Proposal for a Structural Model of the Feline Calicivirus Protease Bound to the Substrate Peptide under Physiological Conditions.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jul 25;8:1383. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01383. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28790989 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial peptide-based epitope mapping from Ebola virus DNA vaccines and infections reveals residue-level determinants of antibody binding.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017 Dec 2;13(12):2953-2966. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2017.1360454. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017. PMID: 28922082 Free PMC article.
-
Increased infectivity in human cells and resistance to antibody-mediated neutralization by truncation of the SIV gp41 cytoplasmic tail.Front Microbiol. 2013 May 14;4:117. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00117. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23717307 Free PMC article.
-
The value of HIV protective epitope research for informed vaccine design against diverse viral pathogens.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2014 Aug;13(8):935-7. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2014.928597. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2014. PMID: 24964950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Igarashi T, Brown C, Azadegan A, Haigwood N, Dimitrov D, Martin MA, Shibata R. 1999. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralizing antibodies accelerate clearance of cell-free virions from blood plasma. Nat. Med. 5:211–216 - PubMed
-
- Shibata R, Igarashi T, Haigwood N, Buckler-White A, Ogert R, Ross W, Willey R, Cho MW, Martin MA. 1999. Neutralizing antibody directed against the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein can completely block HIV-1/SIV chimeric virus infections of macaque monkeys. Nat. Med. 5:204–210 - PubMed
-
- Veazey RS, Shattock RJ, Pope M, Kirijan JC, Jones J, Hu Q, Ketas T, Marx PA, Klasse PJ, Burton DR, Moore JP. 2003. Prevention of virus transmission to macaque monkeys by a vaginally applied monoclonal antibody to HIV-1 gp120. Nat. Med. 9:343–346 - PubMed
-
- Hessell AJ, Rakasz EG, Poignard P, Hangartner L, Landucci G, Forthal DN, Koff WC, Watkins DI, Burton DR. 2009. Broadly neutralizing human anti-HIV antibody 2G12 is effective in protection against mucosal SHIV challenge even at low serum neutralizing titers. PLoS Pathog. 5:e1000433 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000433 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mascola JR, Stiegler G, VanCott TC, Katinger H, Carpenter CB, Hanson CE, Beary H, Hayes D, Frankel SS, Birx DL, Lewis MG. 2000. Protection of macaques against vaginal transmission of a pathogenic HIV-1/SIV chimeric virus by passive infusion of neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Med. 6:207–210 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

