Entamoeba histolytica induces cell death of HT29 colonic epithelial cells via NOX1-derived ROS
- PMID: 23467460
- PMCID: PMC3587751
- DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2013.51.1.61
Entamoeba histolytica induces cell death of HT29 colonic epithelial cells via NOX1-derived ROS
Abstract
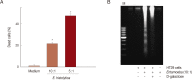
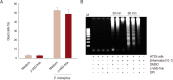
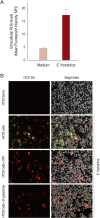
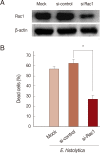
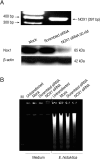
Entamoeba histolytica, which causes amoebic colitis and occasionally liver abscess in humans, is able to induce host cell death. However, signaling mechanisms of colon cell death induced by E. histolytica are not fully elucidated. In this study, we investigated the signaling role of NOX in cell death of HT29 colonic epithelial cells induced by E. histolytica. Incubation of HT29 cells with amoebic trophozoites resulted in DNA fragmentation that is a hallmark of apoptotic cell death. In addition, E. histolytica generate intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a contact-dependent manner. Inhibition of intracellular ROS level with treatment with DPI, an inhibitor of NADPH oxidases (NOXs), decreased Entamoeba-induced ROS generation and cell death in HT29 cells. However, pan-caspase inhibitor did not affect E. histolytica-induced HT29 cell death. In HT29 cells, catalytic subunit NOX1 and regulatory subunit Rac1 for NOX1 activation were highly expressed. We next investigated whether NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1)-derived ROS is closely associated with HT29 cell death induced by E. histolytica. Suppression of Rac1 by siRNA significantly inhibited Entamoeba-induced cell death. Moreover, knockdown of NOX1 by siRNA, effectively inhibited E. histolytica-triggered DNA fragmentation in HT29 cells. These results suggest that NOX1-derived ROS is required for apoptotic cell death in HT29 colon epithelial cells induced by E. histolytica.
Keywords: Entamoeba histolytica; HT29 colon epithelial cell; NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1); host cell death; reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signaling Role of NADPH Oxidases in ROS-Dependent Host Cell Death Induced by Pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica.Korean J Parasitol. 2022 Jun;60(3):155-161. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2022.60.3.155. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Korean J Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35772733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of NOX2-derived ROS in human hepatoma HepG2 cell death induced by Entamoeba histolytica.Parasites Hosts Dis. 2023 Nov;61(4):388-396. doi: 10.3347/PHD.23094. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Parasites Hosts Dis. 2023. PMID: 38043534 Free PMC article.
-
NOX1 participates in ROS-dependent cell death of colon epithelial Caco2 cells induced by Entamoeba histolytica.Microbes Infect. 2011 Nov;13(12-13):1052-61. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.06.001. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Microbes Infect. 2011. PMID: 21723410
-
NOX4 activation is involved in ROS-dependent Jurkat T-cell death induced by Entamoeba histolytica.Parasite Immunol. 2019 Nov;41(11):e12670. doi: 10.1111/pim.12670. Parasite Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31505041
-
Taking a bite: Amoebic trogocytosis in Entamoeba histolytica and beyond.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015 Dec;28:26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2015.07.009. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26277085 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective action of NADPH oxidase inhibitors and role of NADPH oxidase in pathogenesis of colon inflammation in mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep 21;20(35):12533-41. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i35.12533. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25253955 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Role of NADPH Oxidases in ROS-Dependent Host Cell Death Induced by Pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica.Korean J Parasitol. 2022 Jun;60(3):155-161. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2022.60.3.155. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Korean J Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35772733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A whole-genome RNAi screen uncovers a novel role for human potassium channels in cell killing by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 8;5:13613. doi: 10.1038/srep13613. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26346926 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation of the transcription factors NF-κB, STAT3, and STAT5 is involved in Entamoeba histolytica-induced cell death in Caco-2 colonic epithelial cells.Korean J Parasitol. 2014 Oct;52(5):459-69. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2014.52.5.459. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Korean J Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 25352693 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of NOX2-derived ROS in human hepatoma HepG2 cell death induced by Entamoeba histolytica.Parasites Hosts Dis. 2023 Nov;61(4):388-396. doi: 10.3347/PHD.23094. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Parasites Hosts Dis. 2023. PMID: 38043534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stanley SL., Jr Amoebiasis. Lancet. 2003;361:1025–1034. - PubMed
-
- Moncada D, Keller K, Ankri S, Mirelman D, Chadee K. Antisense inhibition of Entamoeba histolytica cysteine proteases inhibits colonic mucus degradation. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:721–730. - PubMed
-
- Petri WA, Haque R, Mann BJ. The bittersweet interface of parasite and host: lectin-carbohydrate interactions during human invasion by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2002;56:39–64. - PubMed
-
- Sim S, Park SJ, Yong TS, Im KI, Shin MH. Involvement of beta 2-integrin in ROS-mediated neutrophil apoptosis induced by Entamoeba histolytica. Microbes Infect. 2007;9:1368–1375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

