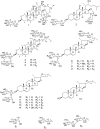
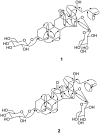
Cholestane steroid glycosides from the rhizomes of Dioscorea villosa (wild yam)
- PMID: 23454141
- PMCID: PMC4009708
- DOI: 10.1016/j.carres.2012.12.022
Cholestane steroid glycosides from the rhizomes of Dioscorea villosa (wild yam)
Abstract
Phytochemical investigation of the MeOH extract of Dioscorea villosa rhizomes resulted in the isolation of two new bidesmosidic cholestane steroid glycosides, dioscoreavillosides A and B (1 and 2). In addition, the extract yielded 12 previously known furostan and spirostan steroid glycosides (3-14), along with diosgenin (15). Compounds 3-7, 9, 14, and 15 were isolated for the first time from D. villosa. The structures of the isolated compounds were determined using spectroscopic and chemical methods including 1D and 2D NMR. The antimicrobial action of most of these compounds was tested against five fungal and five bacterial strains.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cholestane and spirostane glycosides from the rhizomes of Dioscorea septemloba.Phytochemistry. 2008 Apr;69(6):1411-8. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.12.014. Epub 2008 Feb 14. Phytochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18279900
-
Cholestane glycosides and trihydroxy fatty acids from the rhizomes of Dioscorea septemloba.Planta Med. 2010 Feb;76(3):291-4. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1186063. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Planta Med. 2010. PMID: 19708004
-
Two spirostan steroid glycoside fatty esters from Dioscorea cayenensis.Nat Prod Commun. 2013 Mar;8(3):323-6. Nat Prod Commun. 2013. PMID: 23678801 Free PMC article.
-
Steroidal sapogenins and glycosides from the rhizomes of Dioscorea bulbifera.J Nat Prod. 2009 Nov;72(11):1964-8. doi: 10.1021/np900255h. J Nat Prod. 2009. PMID: 19842682
-
Final report of the amended safety assessment of Dioscorea Villosa (Wild Yam) root extract.Int J Toxicol. 2004;23 Suppl 2:49-54. doi: 10.1080/10915810490499055. Int J Toxicol. 2004. PMID: 15513824 Review.
Cited by
-
Physicochemical Properties of Wild Yam (Dioscorea villosa) Starch.Int J Food Sci. 2023 Sep 29;2023:8868218. doi: 10.1155/2023/8868218. eCollection 2023. Int J Food Sci. 2023. PMID: 37810947 Free PMC article.
-
The Dioscorea Genus (Yam)-An Appraisal of Nutritional and Therapeutic Potentials.Foods. 2020 Sep 16;9(9):1304. doi: 10.3390/foods9091304. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32947880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dioscorea Plants: A Genus Rich in Vital Nutra-pharmaceuticals-A Review.Iran J Pharm Res. 2019 Fall;18(Suppl1):68-89. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2019.112501.13795. Iran J Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 32802090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of Neglected and Underutilized Yams (Dioscorea spp.) for Improving Nutritional Security and Health Benefits.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Apr 24;11:496. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00496. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32390842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatoprotective Effect of Steroidal Glycosides From Dioscorea villosa on Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Hepatotoxicity in HepG2 Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jul 23;9:797. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00797. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30083104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu CC, Lin JT, Liu SC, Yang DJ. J Food Drug Anal. 2007;15:310–315.
-
- Liu XT, Wang ZZ, Xiao W, Zhao HW, Hu J, Yu B. Phytochemistry. 2008;69:1411–1418. - PubMed
-
- Shen P, Wang SL, Liu XK, Yang CR, Cai B, Yao XS. J Asian Nat Prod, Res. 2002;4:211–215. - PubMed
-
- Yin J, Kouda K, Tezuka Y, Tran QL, Miyahara T, Chen Y, Kadota S. J Nat Prod. 2003;66:646–650. - PubMed
-
- Teponno RB, Tapondjou AL, Abou-Mansour E, Stoeckli-Evans H, Tane P, Barboni L. Phytochemistry. 2008;69:2374–2379.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources