The severity of experimental arthritis is independent of IL-36 receptor signaling
- PMID: 23452551
- PMCID: PMC3672771
- DOI: 10.1186/ar4192
The severity of experimental arthritis is independent of IL-36 receptor signaling
Abstract
Introduction: Interleukin (IL)-36 refers to three related IL-1 family cytokines, IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ, that bind to the IL-36 receptor (IL-36R). IL-36 exerts proinflammatory effects in skin and lung and stimulates T cell responses. In the present study, we examined the expression and function of IL-36R and its ligands in experimental arthritis.
Methods: Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA), antigen-induced arthritis (AIA), and K/BxN serum transfer-induced arthritis were induced according to standard protocols. Messenger RNA levels for IL-36R and its ligands in the joints of mice with CIA were determined by RT-qPCR. Mice with CIA were injected with a blocking monoclonal anti-IL-36R, a blocking anti-IL-1RI, or their isotype-matched control antibodies at the time of arthritis onset. Anti-IL-36R or control antibodies were also injected at the time of AIA induction. Finally, IL-36R-deficient mice were examined in AIA and serum transfer-induced arthritis. The development and severity of arthritis were assessed by clinical and histological scoring.
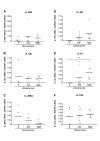
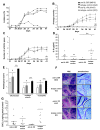
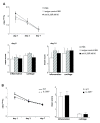
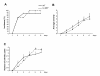
Results: IL-36R, IL-36Ra and IL-36γ mRNA were detected in the joints of mice with CIA, but their levels did not correlate with arthritis severity. As opposed to anti-IL-1RI antibody treatment, the injection of an anti-IL-36R antibody was devoid of effect on the development and severity of CIA. The severity of joint inflammation and structural damage in AIA was also unaltered by anti-IL-36R antibody treatment. Finally, the severity of AIA and K/BxN serum transfer-induced arthritis was similar in IL-36R-deficient and wild-type mice.
Conclusions: The development and severity of experimental arthritis are independent of IL-36R signaling.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of interleukin-33 signaling attenuates the severity of experimental arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Mar;60(3):738-49. doi: 10.1002/art.24305. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19248109
-
Protection against cartilage and bone destruction by systemic interleukin-4 treatment in established murine type II collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res. 1999;1(1):81-91. doi: 10.1186/ar14. Epub 1999 Oct 26. Arthritis Res. 1999. PMID: 11056663 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Salt Diet Attenuates B-Cell- and Myeloid-Cell-Driven Experimental Arthritides by Affecting Innate as Well as Adaptive Immune Mechanisms.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 3;12:765741. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.765741. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34925335 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Role of the IL-36/IL-36R Axis in Multiple Inflammatory Skin Diseases.J Invest Dermatol. 2024 Feb;144(2):206-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2023.11.004. Epub 2024 Jan 7. J Invest Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38189700 Review.
-
IL-36 cytokines and gut immunity.Immunology. 2021 Jun;163(2):145-154. doi: 10.1111/imm.13310. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Immunology. 2021. PMID: 33501638 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of IL-1 Family Cytokines IL-36, IL-37, IL-38 in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comprehensive Review.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jun 20;17:4001-4016. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S474879. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38915806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-β type 2 receptor-mediated modulation of the IL-36 family can be therapeutically targeted in osteoarthritis.Sci Transl Med. 2019 May 8;11(491):eaan2585. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aan2585. Sci Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31068441 Free PMC article.
-
IL-36 cytokines in inflammatory and malignant diseases: not the new kid on the block anymore.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Sep;78(17-18):6215-6227. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03909-4. Epub 2021 Aug 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34365521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effect of interleukin-36 receptor antagonist on liver injury induced by concanavalin A in mice.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 May;23(5):623-628. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.35614.8492. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32742600 Free PMC article.
-
Function and Regulation of IL-36 Signaling in Inflammatory Diseases and Cancer Development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Dec 4;7:317. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00317. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31867327 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barton JL, Herbst R, Bosisio D, Higgins L, Nicklin MJ. A tissue specific IL-1 receptor antagonist homolog from the IL-1 cluster lacks IL-1, IL-1ra, IL-18 and IL-18 antagonist activities. Eur J Immunol. 2000;30:3299–3308. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200011)30:11<3299::AID-IMMU3299>3.0.CO;2-S. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Debets R, Timans JC, Homey B, Zurawski S, Sana TR, Lo S, Wagner J, Edwards G, Clifford T, Menon S, Bazan JF, Kastelein RA. Two novel IL-1 family members, IL-1 delta and IL-1 epsilon, function as an antagonist and agonist of NF-kappa B activation through the orphan IL-1 receptor-related protein 2. J Immunol. 2001;167:1440–1446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

