Human SCARB2 transgenic mice as an infectious animal model for enterovirus 71
- PMID: 23451246
- PMCID: PMC3581494
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057591
Human SCARB2 transgenic mice as an infectious animal model for enterovirus 71
Abstract
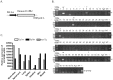
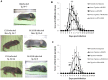
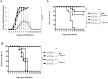
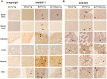
Enterovirus 71 (EV71) and coxsackievirus (CVA) are the most common causative factors for hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) and neurological disorders in children. Lack of a reliable animal model is an issue in investigating EV71-induced disease manifestation in humans, and the current clinical therapies are symptomatic. We generated a novel EV71-infectious model with hSCARB2-transgenic mice expressing the discovered receptor human SCARB2 (hSCARB2). The challenge of hSCARB2-transgenic mice with clinical isolates of EV71 and CVA16 resulted in HFMD-like and neurological syndromes caused by E59 (B4) and N2838 (B5) strains, and lethal paralysis caused by 5746 (C2), N3340 (C4), and CVA16. EV71 viral loads were evident in the tissues and CNS accompanied the upregulated pro-inflammatory mediators (CXCL10, CCL3, TNF-α, and IL-6), correlating to recruitment of the infiltrated T lymphocytes that result in severe diseases. Transgenic mice pre-immunized with live E59 or the FI-E59 vaccine was able to resist the subsequent lethal challenge with EV71. These results indicate that hSCARB2-transgenic mice are a useful model for assessing anti-EV71 medications and for studying the pathogenesis induced by EV71.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Protective efficacy of VP1-specific neutralizing antibody associated with a reduction of viral load and pro-inflammatory cytokines in human SCARB2-transgenic mice.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 30;8(7):e69858. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069858. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936115 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an Enterovirus 71 Vaccine Efficacy Test Using Human Scavenger Receptor B2 Transgenic Mice.J Virol. 2020 Feb 28;94(6):e01921-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01921-19. Print 2020 Feb 28. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31896594 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Murine Model Expressing a Chimeric mSCARB2/hSCARB2 Receptor Is Highly Susceptible to Oral Infection with Clinical Isolates of Enterovirus 71.J Virol. 2019 May 15;93(11):e00183-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00183-19. Print 2019 Jun 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30894476 Free PMC article.
-
Immunocompetent and Immunodeficient Mouse Models for Enterovirus 71 Pathogenesis and Therapy.Viruses. 2018 Nov 28;10(12):674. doi: 10.3390/v10120674. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30487421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Identification of an enterovirus 71 receptor; SCARB2].Uirusu. 2009 Dec;59(2):189-94. doi: 10.2222/jsv.59.189. Uirusu. 2009. PMID: 20218327 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
A new animal model containing human SCARB2 and lacking stat-1 is highly susceptible to EV71.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 8;6:31151. doi: 10.1038/srep31151. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27499235 Free PMC article.
-
Animal Models of Type III Secretion System-Mediated Pathogenesis.Pathogens. 2019 Nov 22;8(4):257. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8040257. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 31766664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A CpG-adjuvanted intranasal enterovirus 71 vaccine elicits mucosal and systemic immune responses and protects human SCARB2-transgenic mice against lethal challenge.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 16;8(1):10713. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28281-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30013088 Free PMC article.
-
Protective efficacy of VP1-specific neutralizing antibody associated with a reduction of viral load and pro-inflammatory cytokines in human SCARB2-transgenic mice.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 30;8(7):e69858. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069858. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936115 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic mouse model for the study of enterovirus 71 neuropathogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Sep 3;110(36):14753-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217563110. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23959904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AbuBakar S, Chee HY, Al-Kobaisi MF, Xiaoshan J, Chua KB, et al. (1999) Identification of enterovirus 71 isolates from an outbreak of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) with fatal cases of encephalomyelitis in Malaysia. Virus Res 61: 1–9. - PubMed
-
- Ho M, Chen ER, Hsu KH, Twu SJ, Chen KT, et al. (1999) An epidemic of enterovirus 71 infection in Taiwan. Taiwan Enterovirus Epidemic Working Group. N Engl J Med 341: 929–935. - PubMed
-
- Lin KH, Hwang KP, Ke GM, Wang CF, Ke LY, et al. (2006) Evolution of EV71 genogroup in Taiwan from 1998 to 2005: an emerging of subgenogroup C4 of EV71. J Med Virol 78: 254–262. - PubMed
-
- Lu CH, Huang SW, Lai YL, Lin CP, Shih CH, et al. (2008) On the relationship between the protein structure and protein dynamics. Proteins 72: 625–634. - PubMed
-
- Melnick JL, Schmidt NJ, Mirkovic RR, Chumakov MP, Lavrova IK, et al. (1980) Identification of Bulgarian strain 258 of enterovirus 71. Intervirology 12: 297–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

