"Seq-ing" insights into the epigenetics of neuronal gene regulation
- PMID: 23439116
- PMCID: PMC3736682
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.01.034
"Seq-ing" insights into the epigenetics of neuronal gene regulation
Abstract
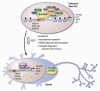
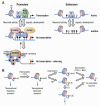
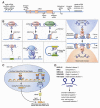
The epigenetic control of neuronal gene expression patterns has emerged as an underlying regulatory mechanism for neuronal function, identity, and plasticity, in which short- to long-lasting adaptation is required to dynamically respond and process external stimuli. To achieve a comprehensive understanding of the physiology and pathology of the brain, it becomes essential to understand the mechanisms that regulate the epigenome and transcriptome in neurons. Here, we review recent advances in the study of regulated neuronal gene expression, which are dramatically expanding as a result of the development of new and powerful contemporary methodologies, based on next-generation sequencing. This flood of new information has already transformed our understanding of many biological processes and is now driving discoveries elucidating the molecular mechanisms of brain function in cognition, behavior, and disease and may also inform the study of neuronal identity, diversity, and neuronal reprogramming.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
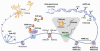

Similar articles
-
Epigenetic mechanisms in mood disorders: targeting neuroplasticity.Neuroscience. 2014 Apr 4;264:112-30. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.01.041. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 23376737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics and function of distal regulatory elements during neurogenesis and neuroplasticity.Genome Res. 2015 Sep;25(9):1309-24. doi: 10.1101/gr.190926.115. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Genome Res. 2015. PMID: 26170447 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the epigenetic language of neuronal plasticity.Neuron. 2008 Dec 26;60(6):961-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.10.012. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 19109904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics of memory and plasticity.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2014;122:305-40. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-420170-5.00011-8. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2014. PMID: 24484706 Review.
-
Epitranscriptomic regulation of transcriptome plasticity in development and diseases of the brain.BMB Rep. 2020 Nov;53(11):551-564. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2020.53.11.204. BMB Rep. 2020. PMID: 33148378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
End of inevitability: programming and reprogramming.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2013 Aug;9(4):385-7. doi: 10.1007/s12015-013-9459-y. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2013. PMID: 23892888
-
System biology approach intersecting diet and cell metabolism with pathogenesis of brain disorders.Prog Neurobiol. 2018 Oct;169:76-90. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Prog Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 30059718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneous transgene expression in the retinas of the TH-RFP, TH-Cre, TH-BAC-Cre and DAT-Cre mouse lines.Neuroscience. 2015 Oct 29;307:319-37. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.08.060. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26335381 Free PMC article.
-
Vision from next generation sequencing: multi-dimensional genome-wide analysis for producing gene regulatory networks underlying retinal development, aging and disease.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015 May;46:1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.01.005. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 25668385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic control of gene regulation during development and disease: A view from the retina.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018 Jul;65:1-27. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 29544768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alarcon JM, Malleret G, Touzani K, Vronskaya S, Ishii S, Kandel ER, Barco A. Chromatin acetylation, memory, and LTP are impaired in CBP+/− mice: a model for the cognitive deficit in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome and its amelioration. Neuron. 2004;42:947–959. - PubMed
-
- Barlow DP. Genomic imprinting: a mammalian epigenetic discovery model. Annual review of genetics. 2011;45:379–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

