NDR2-mediated Rabin8 phosphorylation is crucial for ciliogenesis by switching binding specificity from phosphatidylserine to Sec15
- PMID: 23435566
- PMCID: PMC3604723
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2013.32
NDR2-mediated Rabin8 phosphorylation is crucial for ciliogenesis by switching binding specificity from phosphatidylserine to Sec15
Abstract
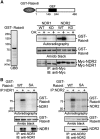
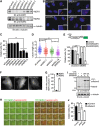
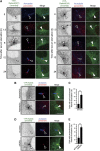
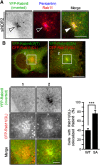
Primary cilia are antenna-like sensory organelles protruding from the plasma membrane. Defects in ciliogenesis cause diverse genetic disorders. NDR2 was identified as the causal gene for a canine ciliopathy, early retinal degeneration, but its role in ciliogenesis remains unknown. Ciliary membranes are generated by transport and fusion of Golgi-derived vesicles to the pericentrosome, a process requiring Rab11-mediated recruitment of Rabin8, a GDP-GTP exchange factor (GEF) for Rab8, and subsequent Rab8 activation and Rabin8 binding to Sec15, a component of the exocyst that mediates vesicle tethering. This study shows that NDR2 phosphorylates Rabin8 at Ser-272 and defects in this phosphorylation impair preciliary membrane assembly and ciliogenesis, resulting in accumulation of Rabin8-/Rab11-containing vesicles at the pericentrosome. Rabin8 binds to and colocalizes with GTP-bound Rab11 and phosphatidylserine (PS) on pericentrosomal vesicles. The phospho-mimetic S272E mutation of Rabin8 decreases affinity for PS but increases affinity for Sec15. These results suggest that NDR2-mediated Rabin8 phosphorylation is crucial for ciliogenesis by triggering the switch in binding specificity of Rabin8 from PS to Sec15, thereby promoting local activation of Rab8 and ciliary membrane formation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The ins and outs of the Arf4-based ciliary membrane-targeting complex.Small GTPases. 2021 Jan;12(1):1-12. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2019.1616355. Epub 2019 May 17. Small GTPases. 2021. PMID: 31068062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Rab8 guanine nucleotide exchange factor-effector interaction network regulates primary ciliogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 4;287(19):15602-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.333245. Epub 2012 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22433857 Free PMC article.
-
The C7orf43/TRAPPC14 component links the TRAPPII complex to Rabin8 for preciliary vesicle tethering at the mother centriole during ciliogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2019 Oct 18;294(42):15418-15434. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008615. Epub 2019 Aug 29. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31467083 Free PMC article.
-
Primary cilia membrane assembly is initiated by Rab11 and transport protein particle II (TRAPPII) complex-dependent trafficking of Rabin8 to the centrosome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 15;108(7):2759-64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018823108. Epub 2011 Jan 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21273506 Free PMC article.
-
Novel topography of the Rab11-effector interaction network within a ciliary membrane targeting complex.Small GTPases. 2015 Oct 2;6(4):165-73. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2015.1091539. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Small GTPases. 2015. PMID: 26399276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fission Yeast NDR/LATS Kinase Orb6 Regulates Exocytosis via Phosphorylation of the Exocyst Complex.Cell Rep. 2019 Feb 5;26(6):1654-1667.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.027. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 30726745 Free PMC article.
-
NDR2 kinase contributes to cell invasion and cytokinesis defects induced by the inactivation of RASSF1A tumor-suppressor gene in lung cancer cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Apr 12;38(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1145-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30979377 Free PMC article.
-
The ins and outs of the Arf4-based ciliary membrane-targeting complex.Small GTPases. 2021 Jan;12(1):1-12. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2019.1616355. Epub 2019 May 17. Small GTPases. 2021. PMID: 31068062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rassf5 and Ndr kinases regulate neuronal polarity through Par3 phosphorylation in a novel pathway.J Cell Sci. 2014 Aug 15;127(Pt 16):3463-76. doi: 10.1242/jcs.146696. Epub 2014 Jun 13. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24928906 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Alterations in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Hope for Effective Treatment by Targeting YAP.Target Oncol. 2022 Jul;17(4):407-431. doi: 10.1007/s11523-022-00900-2. Epub 2022 Jul 30. Target Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35906513 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chiba S, Ikeda M, Katsunuma K, Ohashi K, Mizuno K (2009) MST2- and Furry-mediated activation of NDR1 kinase is critical for precise alignment of mitotic chromosomes. Curr Biol 19: 675–681 - PubMed
-
- Cornils H, Stegert MR, Hergovich A, Hynx D, Schmitz D, Dirnhofer S, Hemmings BA (2010) Ablation of the kinase NDR1 predisposes mice to the development of T cell lymphoma. Sci Signal 3: ra47. - PubMed
-
- Devroe E, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Silver PA (2004) Human Mob proteins regulate the NDR1 and NDR2 serine-threonine kinases. J Biol Chem 279: 24444–24451 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

