Analysis of F2-isoprostanes in plasma of pregnant women by HPLC-MS/MS using a column packed with core-shell particles
- PMID: 23431046
- PMCID: PMC3622342
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.D034553
Analysis of F2-isoprostanes in plasma of pregnant women by HPLC-MS/MS using a column packed with core-shell particles
Abstract
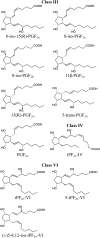
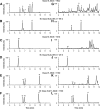
Plasma F2-isoprostanes (F2-isoPs) are reliable biomarkers of oxidative stress. Several possible F2-isoPs are generated by the oxidation of arachidonic acid esterified in phospholipids. The separation of these isomers represents a technical challenge for rapid and selective determination. We have developed a HPLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of seven plasma F2-isoPs, namely 8-iso-15(R)-prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α), 8-iso-PGF2α, 15(R)-PGF2α, iPF2α-IV, iPF2α-VI, 5-iPF2α-VI, and (±)5-8,12-iso-iPF2α-VI. We have validated this method in plasma of pregnant women, a mild physiological oxidative stress known to increase F2-isoPs. Thus, plasma samples of women collected at the third trimester of pregnancy (n = 20) were subjected to alkaline hydrolysis followed by liquid-liquid extraction in order to extract total F2-isoPs. The F2-isoPs were separated within 16.5 min using a column packed with core-shell particles. The class VI isomers were the most abundant, accounting for 65% of the total level of all quantified F2-isoPs in plasma of pregnant women (P < 0.05). The 15(R)-PGF2α was the most abundant of the class III isomers quantified. This method allowed fast and selective separation of seven isomers from three different classes of F2-isoP regioisomers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma F2-isoprostane class VI isomers at 12-18 weeks of pregnancy are associated with later occurrence of preeclampsia.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Aug;85:282-7. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.05.012. Epub 2015 May 19. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25998422 Free PMC article.
-
F2-isoprostanes are correlated with trans fatty acids in the plasma of pregnant women.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2014 Dec;91(6):243-9. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2014. PMID: 25312493 Free PMC article.
-
Increased placental phospholipase A2 gene expression and free F2-isoprostane levels in response to oxidative stress in preeclampsia.Placenta. 2017 Jul;55:54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 May 6. Placenta. 2017. PMID: 28623974
-
Unresolved issues in the analysis of F2-isoprostanes, F4-neuroprostanes, isofurans, neurofurans, and F2-dihomo-isoprostanes in body fluids and tissue using gas chromatography/negative-ion chemical-ionization mass spectrometry.Free Radic Res. 2015;49(7):861-80. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2015.1014812. Epub 2015 Mar 27. Free Radic Res. 2015. PMID: 25812589 Review.
-
Application of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for analysis of isoprostanes: their role in cardiovascular disease.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2003 Dec;41(12):1552-61. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2003.238. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2003. PMID: 14708879 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of MnSOD and GPx1 Genotype at Different Levels of Enteral Nutrition Exposure on Oxidative Stress and Mortality: A Post hoc Analysis From the FeDOx Trial.JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2021 Feb;45(2):287-294. doi: 10.1002/jpen.2012. Epub 2020 Sep 23. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32885455 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Plasma F2-isoprostane class VI isomers at 12-18 weeks of pregnancy are associated with later occurrence of preeclampsia.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Aug;85:282-7. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.05.012. Epub 2015 May 19. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25998422 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Phthalate Metabolites and Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in a Mexican-American Cohort: Variability in Early and Late Pregnancy.Toxics. 2016 Mar;4(1):7. doi: 10.3390/toxics4010007. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Toxics. 2016. PMID: 28008399 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal Oxidative Stress May Affect Fetal Ghrelin Levels in Humans.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 8;5:17881. doi: 10.1038/srep17881. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26643495 Free PMC article.
-
F2-isoprostanes are correlated with trans fatty acids in the plasma of pregnant women.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2014 Dec;91(6):243-9. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2014. PMID: 25312493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schwedhelm E., Bartling A., Lenzen H., Tsikas D., Maas R., Brummer J., Gutzki F. M., Berger J., Frolich J. C., Boger R. H. 2004. Urinary 8-iso-prostaglandin F2alpha as a risk marker in patients with coronary heart disease: a matched case-control study. Circulation. 109: 843–848 - PubMed
-
- Basu S. 2008. F2-isoprostanes in human health and diseases: from molecular mechanisms to clinical implications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 10: 1405–1434 - PubMed
-
- Reilly M. P., Pratico D., Delanty N., DiMinno G., Tremoli E., Rader D., Kapoor S., Rokach J., Lawson J., FitzGerald G. A. 1998. Increased formation of distinct F2 isoprostanes in hypercholesterolemia. Circulation. 98: 2822–2828 - PubMed
-
- Praticò D., Rokach J., Lawson J., FitzGerald G. A. 2004. F2-isoprostanes as indices of lipid peroxidation in inflammatory diseases. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 128: 165–171 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

