Lymphoblastoid cell lines for diagnosis of peroxisome biogenesis disorders
- PMID: 23430824
- PMCID: PMC3509813
- DOI: 10.1007/8904_2011_12
Lymphoblastoid cell lines for diagnosis of peroxisome biogenesis disorders
Abstract
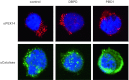
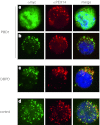
Peroxisome biogenesis disorders (PBDs) are a group of autosomal-recessive developmental and progressive metabolic diseases leading to the Zellweger spectrum (ZS) phenotype in most instances. Diagnosis of clinically suspected cases can be difficult because of extensive genetic heterogeneity and large spectrum of disease severity. Furthermore, a second group of peroxisomal diseases caused by deficiencies of single peroxisomal enzymes can show an indistinguishable clinical phenotype. The diagnosis of these peroxisomal disorders relies on the clinical presentation, the biochemical parameters in plasma and erythrocyte membranes, and genetic testing as the final step. Analysis of patients' cells is frequently required during the diagnostic process, e.g., for complementation analysis to identify the affected gene before sequencing. In the cases with unclear clinical or biochemical presentation, patients' cells are analyzed to prove PBD or to demonstrate biochemical abnormalities that might be elusive in plasma. Cell lines from skin fibroblast that are usually generated for diagnostic workup are not available in all instances, mainly because the required skin biopsy is invasive and sometimes denied by parents. An alternative cellular system has not been analyzed sufficiently. In this study, we evaluated the alternative use of lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs), derived from a peripheral blood sample, in the diagnostic process for PBD. LCLs were suitable for immunofluorescence visualization of peroxisomal enzymes, complementation analysis, and the biochemical analysis to differentiate between control and PBD LCL. LCLs are therefore an easily obtainable alternative cellular system for a detailed PBD diagnostic workup with a reliability of diagnostic results equal to those of skin fibroblasts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peroxisomal disorders I: biochemistry and genetics of peroxisome biogenesis disorders.Clin Genet. 2005 Feb;67(2):107-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2004.00329.x. Clin Genet. 2005. PMID: 15679822 Review.
-
Pharmacological induction of peroxisomes in peroxisome biogenesis disorders.Ann Neurol. 2000 Mar;47(3):286-96. Ann Neurol. 2000. PMID: 10716247
-
Phenotype-genotype relationships in peroxisome biogenesis disorders of PEX1-defective complementation group 1 are defined by Pex1p-Pex6p interaction.Biochem J. 2001 Jul 15;357(Pt 2):417-26. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3570417. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11439091 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the molecular defect in patients with peroxisomal mosaicism using a novel method involving culturing of cells at 40 degrees C: implications for other inborn errors of metabolism.Hum Mutat. 2004 Aug;24(2):130-9. doi: 10.1002/humu.20062. Hum Mutat. 2004. PMID: 15241794
-
Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1299:45-54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-60204-8_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 33417206 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional analysis and molecular characterization of spontaneously outgrown human lymphoblastoid cell lines.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Oct;41(10):6995-7007. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3587-6. Epub 2014 Jul 19. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25037273
References
-
- Duran M, Wanders RJA. Plasmalogens and polyunsaturated fatty acids. In: Blau N, Duran M, Gibson KM, editors. Laboratory guide to the methods in biochemical genetics. Berlin: Springer; 2008. pp. 207–220.
-
- Dursun A, Gucer S, Ebberink MS, Yigit S, Wanders RJ, Waterham HR (2009) Zellweger syndrome with unusual findings: non-immune hydrops fetalis, dermal erythropoiesis and hypoplastic toe nails. J Inherit Metab Dis [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

