Suppression of LFA-1 expression by spermine is associated with enhanced methylation of ITGAL, the LFA-1 promoter area
- PMID: 23418509
- PMCID: PMC3572138
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056056
Suppression of LFA-1 expression by spermine is associated with enhanced methylation of ITGAL, the LFA-1 promoter area
Abstract
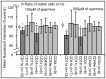
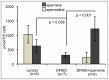
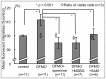
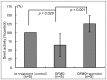
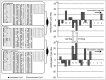
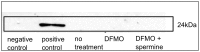
Spermine and spermidine, natural polyamines, suppress lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) expression and its associated cellular functions through mechanisms that remain unknown. Inhibition of ornithine decarboxylase, which is required for polyamine synthesis, in Jurkat cells by 3 mM D,L-alpha-difluoromethylornithine hydrochloride (DFMO) significantly decreased spermine and spermidine concentrations and was associated with decreased DNA methyltransferase (Dnmt) activity, enhanced demethylation of the LFA-1 gene (ITGAL) promoter area, and increased CD11a expression. Supplementation with extracellular spermine (500 µM) of cells pretreated with DFMO significantly increased polyamine concentrations, increased Dnmt activity, enhanced methylation of the ITGAL promoter, and decreased CD11a expression. It has been shown that changes in intracellular polyamine concentrations affect activities of -adenosyl-L-methionine-decaroboxylase, and, as a result, affect concentrations of the methyl group donor, S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), and of the competitive Dnmt inhibitor, decarboxylated SAM. Additional treatments designed to increase the amount of SAM and decrease the amount of decarboxylated SAM-such as treatment with methylglyoxal bis-guanylhydrazone (an inhibitor of S-adenosyl-L-methionine-decaroboxylase) and SAM supplementation-successfully decreased CD11a expression. Western blot analyses revealed that neither DFMO nor spermine supplementation affected the amount of active Ras-proximate-1, a member of the Ras superfamily of small GTPases and a key protein for regulation of CD11a expression. The results of this study suggest that polyamine-induced suppression of LFA-1 expression occurs via enhanced methylation of ITGAL.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polyamine Metabolism and Gene Methylation in Conjunction with One-Carbon Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 10;19(10):3106. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103106. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30309036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Spermine Activates DNA Methyltransferase 3A and 3B.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 12;20(5):1254. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051254. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30871110 Free PMC article.
-
Indirect evidence for a strict negative control of S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase by spermidine in rat hepatoma cells.Biochem J. 1981 May 15;196(2):411-22. doi: 10.1042/bj1960411. Biochem J. 1981. PMID: 6797404 Free PMC article.
-
Spermine, a natural polyamine, suppresses LFA-1 expression on human lymphocyte.J Immunol. 2005 Jul 1;175(1):237-45. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.1.237. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15972654
-
Spermine and gene methylation: a mechanism of lifespan extension induced by polyamine-rich diet.Amino Acids. 2020 Feb;52(2):213-224. doi: 10.1007/s00726-019-02733-2. Epub 2019 Apr 19. Amino Acids. 2020. PMID: 31004229 Review.
Cited by
-
Control of Inflammation by Calorie Restriction Mimetics: On the Crossroad of Autophagy and Mitochondria.Cells. 2019 Dec 28;9(1):82. doi: 10.3390/cells9010082. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31905682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA methylation similarities in genes of black South Africans with systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis.J Biomed Sci. 2015 May 20;22(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12929-015-0142-2. J Biomed Sci. 2015. PMID: 25986394 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamine Metabolism and Gene Methylation in Conjunction with One-Carbon Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 10;19(10):3106. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103106. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30309036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole Blood Spermine/Spermidine Ratio as a New Indicator of Sarcopenia Status in Older Adults.Biomedicines. 2023 May 9;11(5):1403. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051403. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37239074 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of polyamines on the binding of anti-DNA antibodies from patients with SLE and normal human subjects.Clin Immunol. 2014 Jul;153(1):94-103. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2014.04.003. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24732074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hibbs ML, Xu H, Stacker SA, Springer TA (1991) Regulation of adhesion of ICAM-1 by the cytoplasmic domain of LFA-1 integrin beta subunit. Science 251: 1611–1613. - PubMed
-
- Whitcup SM, Chan CC, Kozhich AT, Magone MT (1999) Blocking ICAM-1 (CD54) and LFA-1 (CD11a) inhibits experimental allergic conjunctivitis. Clin Immunol 93: 107–113. - PubMed
-
- Werther WA, Gonzalez TN, O’Connor SJ, McCabe S, Chan B, et al. (1996) Humanization of an anti-lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA)-1 monoclonal antibody and reengineering of the humanized antibody for binding to rhesus LFA-1. J Immunol 157: 4986–4995. - PubMed
-
- Gadek TR, Burdick DJ, McDowell RS, Stanley MS, Marsters JC, et al. (2002) Generation of an LFA-1 antagonist by the transfer of the ICAM-1 immunoregulatory epitope to a small molecule. Science 295: 1086–1089. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

