The non-coding B2 RNA binds to the DNA cleft and active-site region of RNA polymerase II
- PMID: 23416138
- PMCID: PMC3672349
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.01.035
The non-coding B2 RNA binds to the DNA cleft and active-site region of RNA polymerase II
Abstract
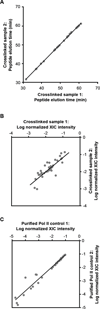
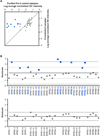
The B2 family of short interspersed elements is transcribed into non-coding RNA by RNA polymerase III. The ~180-nt B2 RNA has been shown to potently repress mRNA transcription by binding tightly to RNA polymerase II (Pol II) and assembling with it into complexes on promoter DNA, where it keeps the polymerase from properly engaging the promoter DNA. Mammalian Pol II is an ~500-kDa complex that contains 12 different protein subunits, providing many possible surfaces for interaction with B2 RNA. We found that the carboxy-terminal domain of the largest Pol II subunit was not required for B2 RNA to bind Pol II and repress transcription in vitro. To identify the surface on Pol II to which the minimal functional region of B2 RNA binds, we coupled multi-step affinity purification, reversible formaldehyde cross-linking, peptide sequencing by mass spectrometry, and analysis of peptide enrichment. The Pol II peptides most highly recovered after cross-linking to B2 RNA mapped to the DNA binding cleft and active-site region of Pol II. These studies determine the location of a defined nucleic acid binding site on a large, native, multi-subunit complex and provide insight into the mechanism of transcriptional repression by B2 RNA.
Keywords: C-terminal domain of RPB1; CTD; EM; EMSA; LC; MS; MS/MS; Pol II; RNA polymerase II; RPB; TATA binding protein; TBP; TFII; XIC; electron microscopy; electrophoretic mobility shift assay; extracted ion chromatogram; liquid chromatography; mass spectrometry; ncRNA; non-coding RNA; protein–RNA cross-linking; subunit of RNA polymerase II; transcription; transcription factor of RNA polymerase II.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Structural insights into transcriptional repression by noncoding RNAs that bind to human Pol II.J Mol Biol. 2013 Oct 9;425(19):3639-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.08.024. Epub 2012 Sep 4. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 22954660 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the structure, function, and mechanism of B2 RNA, an ncRNA repressor of RNA polymerase II transcription.RNA. 2007 Apr;13(4):583-96. doi: 10.1261/rna.310307. Epub 2007 Feb 16. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17307818 Free PMC article.
-
B2 RNA and Alu RNA repress transcription by disrupting contacts between RNA polymerase II and promoter DNA within assembled complexes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Apr 7;106(14):5569-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810738106. Epub 2009 Mar 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19307572 Free PMC article.
-
The Ess1 prolyl isomerase: traffic cop of the RNA polymerase II transcription cycle.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1839(4):316-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24530645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA polymerase II elongation factors use conserved regulatory mechanisms.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024 Feb;84:102766. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2023.102766. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38181687 Review.
Cited by
-
Global profiling of protein-DNA and protein-nucleosome binding affinities using quantitative mass spectrometry.Nat Commun. 2018 Apr 25;9(1):1653. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04084-0. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29695722 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA polymerase II subunit RPB-9 recruits the integrator complex to terminate Caenorhabditis elegans piRNA transcription.EMBO J. 2021 Mar 1;40(5):e105565. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020105565. Epub 2021 Feb 3. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 33533030 Free PMC article.
-
TDP-43 regulates transcription at protein-coding genes and Alu retrotransposons.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019 Oct;1862(10):194434. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.194434. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019. PMID: 31655156 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin-associated ncRNA activities.Chromosome Res. 2013 Dec;21(6-7):627-41. doi: 10.1007/s10577-013-9390-8. Chromosome Res. 2013. PMID: 24249576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two key arginine residues in the coat protein of Bamboo mosaic virus differentially affect the accumulation of viral genomic and subgenomic RNAs.Mol Plant Pathol. 2014 Feb;15(2):196-210. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12080. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Mol Plant Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24393453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kadonaga JT. Regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription by sequence-specific DNA binding factors. Cell. 2004;116:247–257. - PubMed
-
- Li B, Carey M, Workman JL. The role of chromatin during transcription. Cell. 2007;128:707–719. - PubMed
-
- Naar AM, Lemon BD, Tjian R. Transcriptional coactivator complexes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001;70:475–501. - PubMed
-
- Thomas MC, Chiang CM. The general transcription machinery and general cofactors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006;41:105–178. - PubMed
-
- Barrandon C, Spiluttini B, Bensaude O. Non-coding RNAs regulating the transcriptional machinery. Biol. Cell. 2008;100:83–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

