Contribution of the latent transforming growth factor-β binding protein 2 gene to etiology of primary open angle glaucoma and pseudoexfoliation syndrome
- PMID: 23401661
- PMCID: PMC3568400
Contribution of the latent transforming growth factor-β binding protein 2 gene to etiology of primary open angle glaucoma and pseudoexfoliation syndrome
Abstract
Purpose: To assess for the first time the possible contribution of latent transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta binding protein 2 (LTBP2), an extracellular matrix (ECM) protein that associates with fibrillin-1-containing microfibrils, to the etiology of primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) and pseudoexfoliation (PEX) syndrome. Mutations in LTBP2 have previously been shown to be the cause of primary congenital glaucoma (PCG) and other disorders that often manifest as secondary glaucoma.
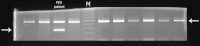
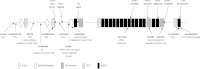
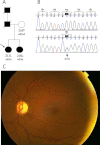
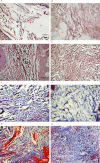
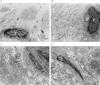
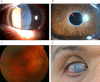
Methods: All exons of LTBP2 were sequenced in the DNA of 42 unrelated patients with POAG and 48 unrelated patients with PEX syndrome. Contribution of candidate variations to disease was assessed by screening in control individuals and use of biochemical, bioinformatics, and evolutionary criteria, and in one case by segregation analysis within the family of a proband with POAG. Microscopy was performed on the skin of a patient with PEX syndrome whose condition developed into PEX glaucoma during the course of the study and on the skin of her son previously identified with PCG who harbored the same LTBP2 mutation.
Results: Among the 30 sequence variations observed in LTBP2, five found in five patients with POAG and two found in two patients with PEX glaucoma syndrome may contribute to their diseases. One of the mutations was observed in a patient with POAG and in a patient with PEX glaucoma syndrome. Light, fluorescent, and electron microscopy showed that a mutation present in one of the individuals affected with PEX glaucoma syndrome and in her son affected with PCG causes disruptions in the ECM.
Conclusions: Some LTBP2 sequence variations can contribute to the etiology of POAG and PEX glaucoma syndrome. It is not expected that in these diseases LTBP2 mutations behave in a strictly Mendelian fashion with complete penetrance. In conjunction with recent findings, the results suggest that anomalies in the ECM are among the factors that can contribute to POAG and PEX glaucoma syndrome. LTBP2 and other related ECM protein coding genes should be screened in larger cohorts with these diseases, which are common disorders and important to the public health.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Exploring functional candidate genes for genetic association in german patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome and pseudoexfoliation glaucoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Jun;50(6):2796-801. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2339. Epub 2009 Jan 31. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19182256
-
Comparative effects of TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2 on extracellular matrix production, proliferation, migration, and collagen contraction of human Tenon's capsule fibroblasts in pseudoexfoliation and primary open-angle glaucoma.Exp Eye Res. 2005 Jan;80(1):121-34. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2004.08.018. Exp Eye Res. 2005. PMID: 15652533
-
Association of IL-10 gene promoter polymorphisms with susceptibility to pseudoexfoliation syndrome, pseudoexfoliative and primary open-angle glaucoma.BMC Med Genet. 2020 Feb 12;21(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12881-020-0969-6. BMC Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 32050932 Free PMC article.
-
[Relevance of the pseudoexfoliation syndrome for the glaucomas].Ophthalmologe. 2002 Sep;99(9):683-90. doi: 10.1007/s00347-002-0702-1. Ophthalmologe. 2002. PMID: 12219256 Review. German.
-
Glaucoma in iran and contributions of studies in iran to the understanding of the etiology of glaucoma.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2015 Jan-Mar;10(1):68-76. doi: 10.4103/2008-322X.156120. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2015. PMID: 26005556 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular matrix in the trabecular meshwork: intraocular pressure regulation and dysregulation in glaucoma.Exp Eye Res. 2015 Apr;133:112-25. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2014.07.014. Exp Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 25819459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular analysis of myocilin and optineurin genes in Korean primary glaucoma patients.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Sep;14(3):2439-48. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5557. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27485216 Free PMC article.
-
Congenital anterior segment ocular disorders: Genotype-phenotype correlations and emerging novel mechanisms.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2024 Sep;102:101288. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2024.101288. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 39097141 Review.
-
Novel ancestry-specific primary open-angle glaucoma loci and shared biology with vascular mechanisms and cell proliferation.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Feb 20;5(2):101430. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101430. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 38382466 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous Humor TGF-β2 and Its Association With Intraocular Pressure in a Naturally Occurring Large Animal Model of Glaucoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Jul 3;64(10):18. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.10.18. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023. PMID: 37459065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali M, McKibbin M, Booth A, Parry DA, Jain P, Riazuddin SA, Hejtmancik JF, Khan SN, Firasat S, Shires M, Gilmour DF, Towns K, Murphy AL, Azmanov D, Tournev I, Cherninkova S, Jafri H, Raashid Y, Toomes C, Craig J, Mackey DA, Kalaydjieva L, Riazuddin S, Inglehearn CF. Null mutations in LTBP2 cause primary congenital glaucoma. Am J Hum Genet. 2009;84:664–71. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Narooie-Nejad M, Paylakhi SH, Shojaee S, Fazlali Z, Rezaei Kanavi M, Nilforushan N, Yazdani S, Babrzadeh F, Suri F, Ronaghi M, Elahi E, Paisan-Ruiz C. Loss of function mutations in the gene encoding latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 2, LTBP2, cause primary congenital glaucoma. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18:3969–77. - PubMed
-
- Kumar A, Duvvari MR, Prabhakaran VC, Shetty JS, Murthy GJ, Blanton SH. A homozygous mutation in LTBP2 causes isolated microspherophakia. Hum Genet. 2010;128:365–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
