LTP requires a unique postsynaptic SNARE fusion machinery
- PMID: 23395379
- PMCID: PMC3569727
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.11.029
LTP requires a unique postsynaptic SNARE fusion machinery
Abstract
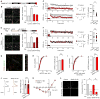
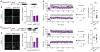
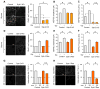
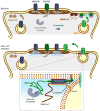
Membrane fusion during exocytosis is mediated by assemblies of SNARE (soluble NSF-attachment protein receptor) and SM (Sec1/Munc18-like) proteins. The SNARE/SM proteins involved in vesicle fusion during neurotransmitter release are well understood, whereas little is known about the protein machinery that mediates activity-dependent AMPA receptor (AMPAR) exocytosis during long-term potentiation (LTP). Using direct measurements of LTP in acute hippocampal slices and an in vitro LTP model of stimulated AMPAR exocytosis, we demonstrate that the Q-SNARE proteins syntaxin-3 and SNAP-47 are required for regulated AMPAR exocytosis during LTP but not for constitutive basal AMPAR exocytosis. In contrast, the R-SNARE protein synaptobrevin-2/VAMP2 contributes to both regulated and constitutive AMPAR exocytosis. Both the central complexin-binding and the N-terminal Munc18-binding sites of syntaxin-3 are essential for its postsynaptic role in LTP. Thus, postsynaptic exocytosis of AMPARs during LTP is mediated by a unique fusion machinery that is distinct from that used during presynaptic neurotransmitter release.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
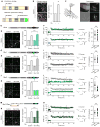
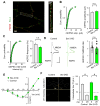
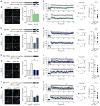
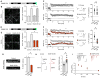
Similar articles
-
Retinoic Acid and LTP Recruit Postsynaptic AMPA Receptors Using Distinct SNARE-Dependent Mechanisms.Neuron. 2015 Apr 22;86(2):442-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.03.009. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Neuron. 2015. PMID: 25843403 Free PMC article.
-
Postsynaptic complexin controls AMPA receptor exocytosis during LTP.Neuron. 2012 Jan 26;73(2):260-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.11.020. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 22284181 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of synaptic NMDA receptors induces membrane insertion of new AMPA receptors and LTP in cultured hippocampal neurons.Neuron. 2001 Jan;29(1):243-54. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00194-5. Neuron. 2001. PMID: 11182095
-
Role of syntaxin 4 in activity-dependent exocytosis and synaptic plasticity in hippocampal neurons.Sci Signal. 2010 Oct 19;3(144):jc7. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.3144jc7. Sci Signal. 2010. PMID: 20959521 Review.
-
Membrane fusion: grappling with SNARE and SM proteins.Science. 2009 Jan 23;323(5913):474-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1161748. Science. 2009. PMID: 19164740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Characterization of AMPA-Receptor-Containing Vesicles.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Oct 15;14:754631. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.754631. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34720876 Free PMC article.
-
Input- and Output-Specific Regulation of Serial Order Performance by Corticostriatal Circuits.Neuron. 2015 Oct 21;88(2):345-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.09.035. Neuron. 2015. PMID: 26494279 Free PMC article.
-
KIF13A drives AMPA receptor synaptic delivery for long-term potentiation via endosomal remodeling.J Cell Biol. 2021 Jun 7;220(6):e202003183. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202003183. Epub 2021 May 17. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33999113 Free PMC article.
-
AMPA-silent synapses in brain development and pathology.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Dec;14(12):839-50. doi: 10.1038/nrn3642. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24201185 Review.
-
GRASP1 Regulates Synaptic Plasticity and Learning through Endosomal Recycling of AMPA Receptors.Neuron. 2017 Mar 22;93(6):1405-1419.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.02.031. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Neuron. 2017. PMID: 28285821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adesnik H, Nicoll RA, England PM. Photoinactivation of native AMPA receptors reveals their real-time trafficking. Neuron. 2005;48:977–985. - PubMed
-
- Blasi J, Chapman ER, Link E, Binz T, Yamasaki S, De Camilli P, Südhof TC, Niemann H, Jahn R. Botulinum neurotoxin A selectively cleaves the synaptic protein SNAP-25. Nature. 1993;365:160–163. - PubMed
-
- Bredt DS, Nicoll RA. AMPA receptor trafficking at excitatory synapses. Neuron. 2003;40:361–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

