Omega-3 fatty acid-derived resolvins and protectins in inflammation resolution and leukocyte functions: targeting novel lipid mediator pathways in mitigation of acute kidney injury
- PMID: 23386851
- PMCID: PMC3558681
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00013
Omega-3 fatty acid-derived resolvins and protectins in inflammation resolution and leukocyte functions: targeting novel lipid mediator pathways in mitigation of acute kidney injury
Abstract
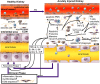
Inflammation, in conjunction with leukocytes, plays a key role in most acute kidney injury (AKI). Non-resolving renal inflammation leads to chronic fibrosis and renal failure. Resolvin D series (RvDs) and E series (RvEs), protectins, and maresins (MaRs) are endogenous omega-3 fatty acid-derived lipid mediators (LMs) that potently promote inflammation resolution by shortening neutrophil life span and promoting macrophage (Mf) non-phelogistic phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and the subsequent exit of Mfs from inflammatory tissue. 14S,21R-dihydroxy docosahexaenoic acid (14S,21R-diHDHA), a Mf-produced autacrine, reprograms Mfs to rescue vascular endothelia. RvD1, RvE1, or 14S,21R-diHDHA also switches Mfs to the phenotype that produces pro-resolving interleukin-10. RvDs or protectin/neuroprotectin D1 (PD1/NPD1) inhibits neutrophil infiltration into injured kidneys, blocks toll-like receptor -mediated inflammatory activation of Mfs and mitigates renal functions. RvDs also repress renal interstitial fibrosis, and PD1 promotes renoprotective heme-oxygenase-1 expression. These findings provide novel approaches for targeting inflammation resolution and LMs or modulation of LM-associated pathways for developing better clinical treatments for AKI.
Keywords: 14S,21R-diHDHA; fibrosis; inflammation-resolution; kidney-injury; leukocytes; maresins; protectins/neuroprotectins; resolvins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resolvin D series and protectin D1 mitigate acute kidney injury.J Immunol. 2006 Nov 1;177(9):5902-11. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.9.5902. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17056514
-
Protectins and maresins: New pro-resolving families of mediators in acute inflammation and resolution bioactive metabolome.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Apr;1851(4):397-413. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Aug 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25139562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous pro-resolving and anti-inflammatory lipid mediators: a new pharmacologic genus.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Mar;153 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S200-15. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707489. Epub 2007 Oct 29. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17965751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
14S,21R-dihydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid treatment enhances mesenchymal stem cell amelioration of renal ischemia/reperfusion injury.Stem Cells Dev. 2012 May 1;21(7):1187-99. doi: 10.1089/scd.2011.0220. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Stem Cells Dev. 2012. PMID: 21846180 Free PMC article.
-
Resolvins, docosatrienes, and neuroprotectins, novel omega-3-derived mediators, and their aspirin-triggered endogenous epimers: an overview of their protective roles in catabasis.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2004 Apr;73(3-4):155-72. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2004.03.005. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2004. PMID: 15290791 Review.
Cited by
-
Animal models and the tumor microenvironment: studies of tumor-host symbiosis.Semin Oncol. 2014 Apr;41(2):146-55. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2014.02.004. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Semin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24787289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Benefits of n-3 PUFA and ɤ-Linolenic Acid in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Nutrients. 2017 Mar 25;9(4):325. doi: 10.3390/nu9040325. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28346333 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
MAFB in Macrophages Regulates Prostaglandin E2-Mediated Lipid Mediator Class Switch through ALOX15 in Ischemic Acute Kidney Injury.J Immunol. 2024 Oct 15;213(8):1212-1224. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300844. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39230290 Free PMC article.
-
The role of resolvin D1 in the regulation of inflammatory and catabolic mediators in osteoarthritis.Inflamm Res. 2016 Aug;65(8):635-45. doi: 10.1007/s00011-016-0946-x. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Inflamm Res. 2016. PMID: 27056390
-
Nutrition facts in multiple sclerosis.ASN Neuro. 2015 Feb 18;7(1):1759091414568185. doi: 10.1177/1759091414568185. Print 2015 Jan-Feb. ASN Neuro. 2015. PMID: 25694551 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ariel A., Chiang N., Arita M., Petasis N. A., Serhan C. N. (2003). Aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4 and B4 analogs block extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent TNF-alpha secretion from human T cells. J. Immunol. 170, 6266–6272 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

