T-cell-specific deletion of Mof blocks their differentiation and results in genomic instability in mice
- PMID: 23386701
- PMCID: PMC3630520
- DOI: 10.1093/mutage/ges080
T-cell-specific deletion of Mof blocks their differentiation and results in genomic instability in mice
Abstract
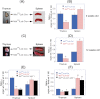
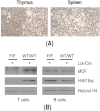
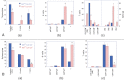
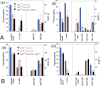
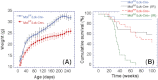
Ataxia telangiectasia patients develop lymphoid malignancies of both B- and T-cell origin. Similarly, ataxia telangiectasia mutated (Atm)-deficient mice exhibit severe defects in T-cell maturation and eventually develop thymomas. The function of ATM is known to be influenced by the mammalian orthologue of the Drosophila MOF (males absent on the first) gene. Here, we report the effect of T-cell-specific ablation of the mouse Mof (Mof) gene on leucocyte trafficking and survival. Conditional Mof(Flox/Flox) (Mof (F/F)) mice expressing Cre recombinase under control of the T-cell-specific Lck proximal promoter (Mof(F/F)/Lck-Cre(+)) display a marked reduction in thymus size compared with Mof(F/F)/Lck-Cre(-) mice. In contrast, the spleen size of Mof(F/F)/Lck-Cre(+) mice was increased compared with control Mof(F/F)/Lck-Cre(-) mice. The thymus of Mof(F/F)/Lck-Cre(+) mice contained significantly reduced T cells, whereas thymic B cells were elevated. Within the T-cell population, CD4(+)CD8(+) double-positive T-cell levels were reduced, whereas the immature CD4(-)CD8(-) double-negative (DN) population was elevated. Defective T-cell differentiation is also evident as an increased DN3 (CD44(-)CD25(+)) population, the cell stage during which T-cell receptor rearrangement takes place. The differentiation defect in T cells and reduced thymus size were not rescued in a p53-deficient background. Splenic B-cell distributions were similar between Mof(F/F)/Lck-Cre(+) and Mof(F/F)/Lck-Cre(-) mice except for an elevation of the κ light-chain population, suggestive of an abnormal clonal expansion. T cells from Mof(F/F)/Lck-Cre(+) mice did not respond to phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) stimulation, whereas LPS-stimulated B cells from Mof(F/F)/Lck-Cre(+) mice demonstrated spontaneous genomic instability. Mice with T-cell-specific loss of MOF had shorter lifespans and decreased survival following irradiation than did Mof(F/F)/Lck-Cre(-) mice. These observations suggest that Mof plays a critical role in T-cell differentiation and that depletion of Mof in T cells reduces T-cell numbers and, by an undefined mechanism, induces genomic instability in B cells through bystander mechanism. As a result, these mice have a shorter lifespan and reduced survival after irradiation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T cell-specific disruption of arylhydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (Arnt) gene causes resistance to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced thymic involution.J Immunol. 2003 Oct 15;171(8):4113-20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.8.4113. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14530333
-
Progression of T cell lineage restriction in the earliest subpopulation of murine adult thymus visualized by the expression of lck proximal promoter activity.Int Immunol. 2001 Jan;13(1):105-17. doi: 10.1093/intimm/13.1.105. Int Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11133839
-
lck-Driven Cre Expression Alters T Cell Development in the Thymus and the Frequencies and Functions of Peripheral T Cell Subsets.J Immunol. 2016 Sep 15;197(6):2261-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600827. Epub 2016 Aug 8. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27503210
-
Fidelity and infidelity in commitment to B-lymphocyte lineage development.Immunol Rev. 2000 Jun;175:104-11. Immunol Rev. 2000. PMID: 10933595 Review.
-
Molecular requirements for lineage commitment in the thymus--antibody-mediated receptor engagements reveal a central role for lck in lineage decisions.Immunol Rev. 1998 Oct;165:181-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1998.tb01239.x. Immunol Rev. 1998. PMID: 9850861 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone H4 lysine 16 acetylated isoform synthesis opens new route to biophysical studies.Proteomics. 2013 May;13(10-11):1546-7. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201300145. Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23595999 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Acetyltransferase MOF Orchestrates Outcomes at the Crossroad of Oncogenesis, DNA Damage Response, Proliferation, and Stem Cell Development.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Aug 28;40(18):e00232-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00232-20. Print 2020 Aug 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32661120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Lck-cre transgene accelerates autoantibody production and lupus development in (NZB × NZW)F1 mice.Lupus. 2016 Feb;25(2):137-54. doi: 10.1177/0961203315603139. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Lupus. 2016. PMID: 26385218 Free PMC article.
-
More complex transcriptional regulation and stress response by MOF.Oncogene. 2016 May;35(21):2681-3. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.373. Epub 2015 Oct 5. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26434593
-
Histone Acetyltransferase Activity of MOF Is Required for MLL-AF9 Leukemogenesis.Cancer Res. 2017 Apr 1;77(7):1753-1762. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2374. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28202522 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

